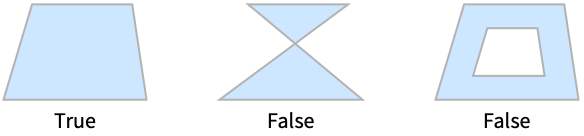
SimplePolygonQ[poly]
gives True if the polygon poly is simple and False otherwise.


SimplePolygonQ
SimplePolygonQ[poly]
gives True if the polygon poly is simple and False otherwise.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Scope (5)
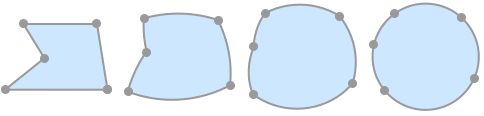
SimplePolygonQ works on polygons:
Applications (2)
Properties & Relations (5)
The OuterPolygon of a simple polygon is simple:
Simple polygons do not have holes:
Use PolygonDecomposition to decompose a polygon into simple polygons:
Use RandomPolygon to generate a simple polygon:
The number of edges of a simple polygon always equals the number of vertices:
Possible Issues (1)
For nonconstant polygons, SimplePolygonQ returns False:
Related Guides
-
▪
- Polygons
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2019), SimplePolygonQ, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/SimplePolygonQ.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2019. "SimplePolygonQ." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/SimplePolygonQ.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2019). SimplePolygonQ. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/SimplePolygonQ.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_simplepolygonq, author="Wolfram Research", title="{SimplePolygonQ}", year="2019", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/SimplePolygonQ.html}", note=[Accessed: 02-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_simplepolygonq, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={SimplePolygonQ}, year={2019}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/SimplePolygonQ.html}, note=[Accessed: 02-March-2026]}