WaveletScalogram
WaveletScalogram[wd]
plots wavelet vector coefficients in a DiscreteWaveletData or ContinuousWaveletData object wd.
WaveletScalogram[wd,wind]
plots wavelet coefficients corresponding to the wavelet index specification wind.
WaveletScalogram[wd,wind,func]
applies func to coefficients before plotting.
Details and Options

- WaveletScalogram plots the transform coefficients as rows of colorized rectangles, in which large absolute values are shown darker and each subsequent row corresponds to different wavelet index specifications.
- The wavelet index specification wind is the same as used by DiscreteWaveletData or ContinuousWaveletData.
- WaveletScalogram[wd] is equivalent to WaveletScalogram[wd,Automatic].
- The following special values can be used for func:
-
"AbsoluteGlobal" absolute value divided by the maximal coefficient "AbsoluteLevel" absolute value divided by the maximal level coefficient - WaveletScalogram has the same options as Graphics, with the following additions and changes: [List of all options]
-
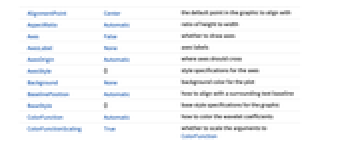
ColorFunction Automatic how to color the wavelet coefficients ColorFunctionScaling True whether to scale the arguments to ColorFunction - WaveletScalogram returns a Graphics object.
-
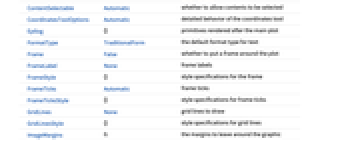
AlignmentPoint Center the default point in the graphic to align with AspectRatio Automatic ratio of height to width Axes False whether to draw axes AxesLabel None axes labels AxesOrigin Automatic where axes should cross AxesStyle {} style specifications for the axes Background None background color for the plot BaselinePosition Automatic how to align with a surrounding text baseline BaseStyle {} base style specifications for the graphic ColorFunction Automatic how to color the wavelet coefficients ColorFunctionScaling True whether to scale the arguments to ColorFunction ContentSelectable Automatic whether to allow contents to be selected CoordinatesToolOptions Automatic detailed behavior of the coordinates tool Epilog {} primitives rendered after the main plot FormatType TraditionalForm the default format type for text Frame False whether to put a frame around the plot FrameLabel None frame labels FrameStyle {} style specifications for the frame FrameTicks Automatic frame ticks FrameTicksStyle {} style specifications for frame ticks GridLines None grid lines to draw GridLinesStyle {} style specifications for grid lines ImageMargins 0. the margins to leave around the graphic ImagePadding All what extra padding to allow for labels etc. ImageSize Automatic the absolute size at which to render the graphic LabelStyle {} style specifications for labels Method Automatic details of graphics methods to use PlotLabel None an overall label for the plot PlotRange All range of values to include PlotRangeClipping False whether to clip at the plot range PlotRangePadding Automatic how much to pad the range of values PlotRegion Automatic the final display region to be filled PreserveImageOptions Automatic whether to preserve image options when displaying new versions of the same graphic Prolog {} primitives rendered before the main plot RotateLabel True whether to rotate y labels on the frame Ticks Automatic axes ticks TicksStyle {} style specifications for axes ticks
List of all options

Examples
open allclose allScope (10)
DiscreteWaveletData (6)
Plot a discrete wavelet scalogram:
The vertical axis represents refinement level and the horizontal axis represents time:
Use Full ticks to expand the labels on the vertical axis:
Specify wavelet indices to plot:
Show wavelet transform as a tree:
The second argument is used to specify wavelet indices:
Scale wavelet coefficients before plotting:
The third argument is used to specify a scaling function:
A scalogram gives a visual representation of a wavelet transform:
Darker colors indicate larger coefficients and lighter colors indicate smaller coefficients:
Use WaveletListPlot to complement a scalogram:
Color variations in the scalogram can be better visualized using WaveletListPlot:
WaveletScalogram works on DiscreteWaveletData generated from any transform:
Plot a scalogram for DiscreteWaveletTransform and DiscreteWaveletPacketTransform:
Plot a scalogram for StationaryWaveletTransform and StationaryWaveletPacketTransform:
ContinuousWaveletData (4)
Plot a continuous wavelet scalogram:
The vertical axis represents scales and the horizontal axis represents time:
Use Full ticks to expand the labels on the vertical axis:
Specify wavelet indices to plot:
The second argument is used to specify wavelet indices:
Scale wavelet coefficients before plotting:
The third argument is used to specify a scaling function:
A single frequency shows up as a horizontal band at the equivalent scale:
Multiple frequencies show up as multiple bands at the equivalent scales:
Options (18)
AxesOrigin (2)
The Automatic setting for AxesOrigin is set to {0,0}:
Coordinates for vertical axes start from 0 at the bottom:
Put the axis origin at ![]() and
and ![]() , which is indicated by the 5
, which is indicated by the 5![]() refinement level:
refinement level:
ColorFunctionScaling (2)
No argument scaling on the left; automatic scaling on the right:
To use ColorFunction with a wider range, set ColorFunctionScaling to False:
Frame (3)
FrameTicks (3)
Place frame ticks on all the edges:
Use Full ticks to draw labels indicating octaves and voices {oct,voc} on the vertical axis:
Label frame ticks to indicate octaves:
Specify overall frame ticks style, including frame tick labels, using FrameTicksStyle:
GridLines (3)
Method (2)
Use a nonlinear raster function as used by MatrixPlot:
Invert wavelet coefficients of DiscreteWaveletData:
Applications (2)
WaveletScalogram can be used to visualize discontinuities:
Plot scalogram for only detail coefficients:
Visualize time scale representation of multiple frequencies:
Higher frequencies are resolved at lower octaves and lower frequencies at higher octaves:
Properties & Relations (2)
Ticks->Automatic indicates refinement level for DiscreteWaveletData on the vertical axis:
Ticks->Full indicates wavelet index specification:
Ticks->Automatic indicates refinement level for ContinuousWaveletData on the vertical axis:
Ticks->Full indicates wavelet octave and voice specification:
Neat Examples (2)
Draw contours over WaveletScalogram:
Use ListPlot3D to visualize a wavelet scalogram in three-dimensional space:
Text
Wolfram Research (2010), WaveletScalogram, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/WaveletScalogram.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2010. "WaveletScalogram." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/WaveletScalogram.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2010). WaveletScalogram. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/WaveletScalogram.html