gives the logistic sigmoid function.




LogisticSigmoid
gives the logistic sigmoid function.
Details
- Mathematical function, suitable for both symbolic and numeric manipulation.
- In TraditionalForm, the logistic sigmoid function is sometimes denoted as
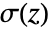 .
. - The logistic function
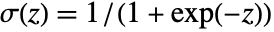 is a solution to the differential equation
is a solution to the differential equation 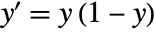 .
. - LogisticSigmoid[z] has no branch cut discontinuities.
- LogisticSigmoid can be evaluated to arbitrary numerical precision.
- LogisticSigmoid automatically threads over lists. »
- LogisticSigmoid can be used with Interval and CenteredInterval objects. »
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (5)
Scope (36)
Numerical Evaluation (6)
The precision of the output tracks the precision of the input:
Evaluate efficiently at high precision:
Compute worst-case guaranteed intervals using Interval and CenteredInterval objects:
Or compute average-case statistical intervals using Around:
Compute the elementwise values of an array using automatic threading:
Or compute the matrix LogisticSigmoid function using MatrixFunction:
Specific Values (4)
The value of LogisticSigmoid at 2 πI n for integer n is 1/2:
Simple exact values are generated automatically:
More complicated cases require explicit use of FunctionExpand:
Find a value of ![]() for which the
for which the ![]() using Solve:
using Solve:
Visualization (3)
Plot the LogisticSigmoid[x] function:
Function Properties (10)
LogisticSigmoid is defined for all real and complex values:
LogisticSigmoid achieves all values between 0 and 1 on the reals:
LogisticSigmoid has the mirror property ![]() :
:
LogisticSigmoid is an analytic function of x:
It has no singularities or discontinuities:
LogisticSigmoid is nondecreasing:
LogisticSigmoid is injective:
LogisticSigmoid is not surjective:
LogisticSigmoid is non-negative:
LogisticSigmoid is neither convex nor concave:
TraditionalForm formatting:
Differentiation (3)
Integration (3)
Compute the indefinite integral using Integrate:
Series Expansions (3)
Function Representations (4)
LogisticSigmoid can be represented in terms of Exp:
LogisticSigmoid can be represented in terms of MeijerG:
LogisticSigmoid obeys the logistic differential equation ![]() :
:
Applications (1)
Write a specific solution to the dimensionless logistic equation using LogisticSigmoid:
See Also
Exp LogisticDistribution UnitStep HeavisideTheta
Function Repository: Logit SmoothStep RationalSmoothStep
Related Guides
Related Links
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2014), LogisticSigmoid, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/LogisticSigmoid.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2014. "LogisticSigmoid." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/LogisticSigmoid.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2014). LogisticSigmoid. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/LogisticSigmoid.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_logisticsigmoid, author="Wolfram Research", title="{LogisticSigmoid}", year="2014", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/LogisticSigmoid.html}", note=[Accessed: 09-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_logisticsigmoid, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={LogisticSigmoid}, year={2014}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/LogisticSigmoid.html}, note=[Accessed: 09-March-2026]}