ZTransform[expr,n,z]
gives the Z transform of expr.
ZTransform[expr,{n1,…,nm},{z1,…,zm}]
gives the multidimensional Z transform of expr.


ZTransform
ZTransform[expr,n,z]
gives the Z transform of expr.
ZTransform[expr,{n1,…,nm},{z1,…,zm}]
gives the multidimensional Z transform of expr.
Details and Options

- The Z transform for a discrete function
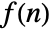 is given by
is given by 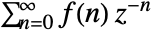 .
. - The multidimensional Z transform is given by
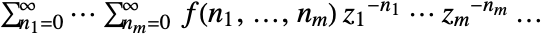 .
. - The following options can be given:
-
Assumptions $Assumptions assumptions to make about parameters GenerateConditions False whether to generate answers that involve conditions on parameters Method Automatic method to use VerifyConvergence True whether to verify convergence - In TraditionalForm, ZTransform is output using .
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (3)
Scope (25)
Basic Uses (7)
Transform a univariate sequence:
Transform a multivariate sequence:
Plot the magnitude using Plot3D, ContourPlot, or DensityPlot:
Generate conditions for the region of convergence:
Evaluate the transform at a point:
Plot both the spectrum and the plot phase using color:
Plot the spectrum in the complex plane using ParametricPlot3D:
ZTransform will use several properties including linearity:
Multiplication by exponentials:
Multiplication by polynomials:
ZTransform automatically threads over lists:
TraditionalForm typesetting:
Special Sequences (13)
Polynomials result in rational transforms:
Factorial exponential polynomials:
Trigonometric, exponential and polynomial:
Combinations of the previous input will also generate rational transforms:
Different ways of expressing piecewise defined signals:
Rational exponential functions:
Hypergeometric term sequences:
The DiscreteRatio is rational for all hypergeometric term sequences:
Many functions give hypergeometric terms:
Any products are hypergeometric terms:
Transforms of hypergeometric terms:
A holonomic sequence is defined by a linear difference equation:
Many special function are holonomic sequences in their index:
Special Operators (5)
There are several relations to the InverseZTransform:
Options (4)
Assumptions (1)
Without assumptions, typically a general formula will be produced:
Use Assumptions to obtain the expression on a given range:
GenerateConditions (1)
Set GenerateConditions to True to get the region of convergence:
VerifyConvergence (1)
By default, convergence testing is performed:
Setting VerifyConvergence->False will avoid the verification step:
Properties & Relations (6)
ZTransform is closely related to GeneratingFunction:
ExponentialGeneratingFunction:
Use InverseZTransform to get the sequence from its transform:
ZTransform effectively computes an infinite sum:
Possible Issues (1)
A ZTransform may not converge for all values of parameters:
Use GenerateConditions to get the region of convergence:
Tech Notes
Related Guides
Related Links
History
Introduced in 1999 (4.0) | Updated in 2008 (7.0)
Text
Wolfram Research (1999), ZTransform, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ZTransform.html (updated 2008).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 1999. "ZTransform." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2008. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ZTransform.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (1999). ZTransform. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ZTransform.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_ztransform, author="Wolfram Research", title="{ZTransform}", year="2008", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ZTransform.html}", note=[Accessed: 09-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_ztransform, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={ZTransform}, year={2008}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ZTransform.html}, note=[Accessed: 09-March-2026]}