FunctionMeromorphic[f,x]
tests whether ![]() is a meromorphic function of x.
is a meromorphic function of x.
FunctionMeromorphic[f,{x1,x2,…}]
tests whether ![]() is a meromorphic function of x1,x2,….
is a meromorphic function of x1,x2,….
FunctionMeromorphic[{f1,f2,…},{x1,x2,…}]
tests whether ![]() are meromorphic functions for x1,x2,….
are meromorphic functions for x1,x2,….
FunctionMeromorphic[{funs,cons},xvars]
tests whether ![]() are meromorphic functions for xvars in an open set containing the solutions of the constraints cons.
are meromorphic functions for xvars in an open set containing the solutions of the constraints cons.


FunctionMeromorphic
FunctionMeromorphic[f,x]
tests whether ![]() is a meromorphic function of x.
is a meromorphic function of x.
FunctionMeromorphic[f,{x1,x2,…}]
tests whether ![]() is a meromorphic function of x1,x2,….
is a meromorphic function of x1,x2,….
FunctionMeromorphic[{f1,f2,…},{x1,x2,…}]
tests whether ![]() are meromorphic functions for x1,x2,….
are meromorphic functions for x1,x2,….
FunctionMeromorphic[{funs,cons},xvars]
tests whether ![]() are meromorphic functions for xvars in an open set containing the solutions of the constraints cons.
are meromorphic functions for xvars in an open set containing the solutions of the constraints cons.
Details and Options

- A function
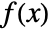 is meromorphic if it can be represented as
is meromorphic if it can be represented as 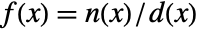 , where
, where 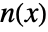 and
and 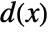 are complex analytic functions.
are complex analytic functions. - A function
 is meromorphic if it can be locally represented as
is meromorphic if it can be locally represented as 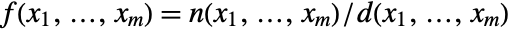 , where
, where  and
and  are complex analytic functions.
are complex analytic functions. - If funs contains parameters other than xvars, the result is typically a ConditionalExpression.
- cons can contain inequalities or logical combinations of these.
- The following options can be given:
-
Assumptions $Assumptions assumptions on parameters GenerateConditions True whether to generate conditions on parameters PerformanceGoal $PerformanceGoal whether to prioritize speed or quality - Possible settings for GenerateConditions include:
-
Automatic nongeneric conditions only True all conditions False no conditions None return unevaluated if conditions are needed - Possible settings for PerformanceGoal are "Speed" and "Quality".
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (3)
Scope (4)
Options (4)
Assumptions (1)
FunctionMeromorphic cannot find the answer for arbitrary values of the parameter ![]() :
:
With the assumption that ![]() is a positive integer, FunctionMeromorphic succeeds:
is a positive integer, FunctionMeromorphic succeeds:
GenerateConditions (2)
By default, FunctionMeromorphic may generate conditions on symbolic parameters:
With GenerateConditions->None, FunctionMeromorphic fails instead of giving a conditional result:
This returns a conditionally valid result without stating the condition:
By default, all conditions are reported:
With GenerateConditions->Automatic, conditions that are generically true are not reported:
PerformanceGoal (1)
Use PerformanceGoal to avoid potentially expensive computations:
The default setting uses all available techniques to try to produce a result:
Applications (12)
Classes of Meromorphic Functions (7)
Rational functions are meromorphic:
Tan, Sec and Sech are meromorphic:
Visualizing the functions in a plane shows that their singularities are no worse than poles:
Functions with branch cuts like Log are not meromorphic:
Neither are Sqrt or any noninteger power:
Inverse trigonometric and hyperbolic functions like ArcSin, ArcTan and ArcCsch are similarly non-meromorphic:
Non-differentiable functions like Abs, Sign and Re are not meromorphic:
Visualize some of these functions:
Functions that are only defined for real inputs, like UnitStep and TriangleWave, cannot be meromorphic:
These functions are not defined for complex value:
Every function analytic in the complex plane is meromorphic:
Arithmetic combinations of meromorphic functions are meromorphic:
As all trigonometric and hyperbolic functions are arithmetic combinations of Exp, they are all meromorphic:
More generally, any rational combination of meromorphic functions is meromorphic:
Visualize Exp and the eight nonanalytic trigonometric and hyperbolic functions:
The compositions of meromorphic functions need not be meromorphic:
The singularities of a meromorphic might bunch up under composition, leading to a non-pole singularity:
There is an essential singularity at the origin, as evidenced by the following limit:
However, the composition of a meromorphic function with an analytic function is always meromorphic:
Visualize the composite functions:
Multivariate rational functions are meromorphic:
Unlike functions of a single variable, singularities lie along curves, in the first function along ![]() :
:
Plotting the second function in the ![]() plane shows the blowup along the hyperbolas
plane shows the blowup along the hyperbolas ![]() :
:
By composing with analytic univariate functions, many more analytic functions can be generated:
The complete Beta function ![]() is meromorphic:
is meromorphic:
It can be considered a multivariate rational function in Gamma:
Integrating Functions (5)
The Limit of a meromorphic function is always either a number or ComplexInfinity:
Sqrt has points where the limit does not exist, so it cannot be meromorphic:
The singular points of a meromorphic function, called poles, have a Residue associated with them:
The residue is the coefficient of ![]() in the power series expansion of the function:
in the power series expansion of the function:
The integral of a meromorphic function around a closed contour equals ![]() times the sum of the residues of the poles enclosed by by the curve. Compute the integral of
times the sum of the residues of the poles enclosed by by the curve. Compute the integral of ![]() around the origin, which is clearly its only pole:
around the origin, which is clearly its only pole:
This must equal ![]() the residue at
the residue at ![]() :
:
Any other closed contour would give the same result, for example, a circular one:
Visualize the function and the contours:
If the contour does not enclose the singularity, the integral will be zero:
Visualize the function with this alternate contour:
If all the singular points of a function have the same or related residues, integrals over a closed contour can be used to count the number of poles enclosed. For example, ![]() has a pole with residue
has a pole with residue ![]() at every half-integer multiple of
at every half-integer multiple of ![]() :
:
The integral of ![]() over a rectangle straddling the real axis counts the number of half-integer multiples of
over a rectangle straddling the real axis counts the number of half-integer multiples of ![]() enclosed:
enclosed:
A common application of contour integrals is to evaluate integrals over the real line, by extending the contour to a closed one with a semicircle in the upper or lower half-plane. If the portion of the integral over the semicircle vanishes, the contour integral must equal the real integral. Consider ![]() . The integrand is meromorphic:
. The integrand is meromorphic:
The singularities of the integrand occur where the denominator is zero:
Complete the contour using a semicircle in the upper half-plane and compute the integral using residues:
The integral over the semicircle is of order ![]() as
as ![]() , so the real integral must have the same value:
, so the real integral must have the same value:
For integrands of the form ![]() with
with ![]() ,
, ![]() meromorphic,
meromorphic, ![]() continuous on
continuous on ![]() , and
, and ![]() for large
for large ![]() , the integral
, the integral ![]() can be computed as
can be computed as ![]() times the sum of the residues of
times the sum of the residues of ![]() in the upper half-plane. Use this to compute
in the upper half-plane. Use this to compute ![]() . First, verify that
. First, verify that ![]() is meromorphic:
is meromorphic:
The function also decays at infinity as is required:
There is a single pole in the upper half-plane at ![]() :
:
Properties & Relations (5)
A meromorphic function is differentiable arbitrarily many times:
Use D to compute derivatives:
A meromorphic function can be expressed as a Taylor series at each point of its domain:
Use Series to compute initial terms of the Taylor series:
The resulting polynomial approximates ![]() near
near ![]() :
:
At its poles, the function can be expressed as a Laurent series with a finite principal part:
A meromorphic function can have only finitely many zeros and poles in a compact region:
Use Solve to find the zeros of ![]() in the unit disk:
in the unit disk:
Use FunctionSingularities to find the poles of ![]() in the unit disk:
in the unit disk:
Plot ![]() , its zeros (blue) and its poles (red):
, its zeros (blue) and its poles (red):
The argument principle states that the difference between the number of zeros and the number of poles of ![]() (counted with multiplicities) is given by
(counted with multiplicities) is given by ![]() . Use NIntegrate to compute
. Use NIntegrate to compute ![]() :
:
Verify that all ![]() are simple zeros of
are simple zeros of ![]() :
:
Use Limit to verify that all ![]() are simple poles of
are simple poles of ![]() :
:
A quotient of complex analytic functions is meromorphic:
Use FunctionAnalytic to check that ![]() and
and ![]() are analytic:
are analytic:
Verify that ![]() and
and ![]() are meromorphic:
are meromorphic:
Meromorphic functions may not be complex analytic:
The only singularities a meromorphic function can have are poles and removable singularities:
Use FunctionSingularities to find a condition satisfied by all singularities:
Use SolveValues to find the singularities:
Use FunctionPoles to find the poles and their multiplicities:
Use ResidueSum to compute the sum of residues in the right half-plane:
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2020), FunctionMeromorphic, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FunctionMeromorphic.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2020. "FunctionMeromorphic." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FunctionMeromorphic.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2020). FunctionMeromorphic. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FunctionMeromorphic.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_functionmeromorphic, author="Wolfram Research", title="{FunctionMeromorphic}", year="2020", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FunctionMeromorphic.html}", note=[Accessed: 28-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_functionmeromorphic, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={FunctionMeromorphic}, year={2020}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FunctionMeromorphic.html}, note=[Accessed: 28-February-2026]}