



Gamma
Details

- Mathematical function, suitable for both symbolic and numerical manipulation.
- The gamma function satisfies
![TemplateBox[{z}, Gamma]=int_0^inftyt^(z-1)e^(-t)dt TemplateBox[{z}, Gamma]=int_0^inftyt^(z-1)e^(-t)dt](Files/Gamma.en/4.png) .
. - The incomplete gamma function satisfies
![TemplateBox[{a, z}, Gamma2]=int_z^inftyt^(a-1)e^(-t)dt TemplateBox[{a, z}, Gamma2]=int_z^inftyt^(a-1)e^(-t)dt](Files/Gamma.en/5.png) .
. - The generalized incomplete gamma function is given by the integral
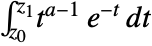 .
. - Note that the arguments in the incomplete form of Gamma are arranged differently from those in the incomplete form of Beta.
- Gamma[z] has no branch cut discontinuities.
- Gamma[a,z] has a branch cut discontinuity in the complex z plane running from
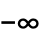 to
to 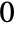 .
. - For certain special arguments, Gamma automatically evaluates to exact values.
- Gamma can be evaluated to arbitrary numerical precision.
- Gamma automatically threads over lists.
- Gamma can be used with Interval and CenteredInterval objects. »
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (8)
Evaluate numerically for complex arguments:
Plot over a subset of the reals:
Plot over a subset of the complexes:
Series expansion at the origin:
Series expansion at Infinity:
Scope (50)
Numerical Evaluation (5)
The precision of the output tracks the precision of the input:
Evaluate Gamma efficiently at high precision:
Compute worst-case guaranteed intervals using Interval and CenteredInterval objects:
Compute average-case statistical intervals using Around:
Compute the elementwise values of an array:
Or compute the matrix Gamma function using MatrixFunction:
Specific Values (5)
Singular points of Gamma:
Find a local minimum as a root of ![]() :
:
Evaluate the incomplete gamma function symbolically at integer and half‐integer orders:
Evaluate the generalized incomplete gamma function symbolically at half‐integer orders:
Visualization (3)
Function Properties (10)
Real domain of the complete Euler gamma function:
Domain of the incomplete gamma functions:
The gamma function ![]() achieves all nonzero values on the reals:
achieves all nonzero values on the reals:
The incomplete gamma function ![]() achieves all positive real values for real inputs:
achieves all positive real values for real inputs:
On the complexes, however, it achieves all nonzero values:
The incomplete gamma function ![]() has the restricted range
has the restricted range ![]() :
:
The Euler gamma function has the mirror property ![]() :
:
The complete gamma function ![]() is a meromorphic, nonanalytic function:
is a meromorphic, nonanalytic function:
![]() is analytic in
is analytic in ![]() for positive integer
for positive integer ![]() :
:
But in general, it is neither an analytic nor a meromorphic function:
![]() has both singularities and discontinuities on the non-positive integers:
has both singularities and discontinuities on the non-positive integers:
![]() is neither non-increasing nor non-decreasing:
is neither non-increasing nor non-decreasing:
![]() is a non-increasing function of
is a non-increasing function of ![]() when
when ![]() is a positive, odd integer:
is a positive, odd integer:
But in general, it is neither non-increasing nor non-decreasing:
![]() is an injective function of
is an injective function of ![]() for noninteger
for noninteger ![]() :
:
For integer ![]() , it may or may not be injective in
, it may or may not be injective in ![]() :
:
![]() is neither non-negative nor non-positive:
is neither non-negative nor non-positive:
![]() is non-negative for positive odd
is non-negative for positive odd ![]() :
:
In general, it is neither non-negative nor non-positive:
![]() is neither convex nor concave:
is neither convex nor concave:
![]() is convex on its real domain for
is convex on its real domain for ![]() :
:
It is in general neither convex nor concave for other values of ![]() :
:
Differentiation (4)
Integration (3)
Series Expansions (6)
Taylor expansion for the Euler gamma function around ![]() :
:
Plot the first three approximations for the Euler gamma function around ![]() :
:
Series expansion at infinity for the Euler gamma function (Stirling approximation):
Give the result for an arbitrary symbolic direction:
Series expansion for the incomplete gamma function at a generic point:
Series expansion for the incomplete gamma function at infinity:
Series expansion for the generalized incomplete gamma function at a generic point:
Gamma can be applied to a power series:
Integral Transforms (4)
Compute the Laplace transform of the incomplete gamma function using LaplaceTransform:
InverseLaplaceTransform of the incomplete gamma function:
MellinTransform of the incomplete gamma function:
InverseMellinTransform of the Euler gamma function:
Function Identities and Simplifications (5)
Use FullSimplify to simplify gamma functions:
The Euler gamma function basic relation, ![]() :
:
Function Representations (5)
Integral representation of the Euler gamma function:
Integral representation of the incomplete gamma function:
The incomplete gamma function can be represented in terms of MeijerG:
The incomplete gamma function can be represented as a DifferentialRoot:
TraditionalForm formatting:
Generalizations & Extensions (6)
Euler Gamma Function (3)
Gamma threads element-wise over lists:
Expansion at symbolically specified negative integers:
TraditionalForm formatting:
Applications (9)
Plot of the absolute value of Gamma in the complex plane:
Find the asymptotic expansion of ratios of gamma functions:
Volume of an ![]() ‐dimensional unit hypersphere:
‐dimensional unit hypersphere:
Plot the volume of the unit hypersphere as a function of dimension:
Plot the real part of the incomplete gamma function over the parameter plane:
Plot the CDF for different numbers of degrees of freedom:
Compute derivatives of the Gamma function with the BellY polynomial:
Compute ![]() as a limit of Gamma functions at Infinity:
as a limit of Gamma functions at Infinity:
Expectation value of the square root of a quadratic form over a normal distribution:
Compare with the closed-form result in terms of Gamma and CarlsonRG:
Represent Zeta in terms of Integrate and the Gamma function:
Properties & Relations (7)
Use FullSimplify to simplify gamma functions:
Numerically find a root of a transcendental equation:
Sum expressions involving Gamma:
Generate from integrals, products, and limits:
Obtain Gamma as the solution of a differential equation:
Gamma can be represented as a DifferenceRoot:
Possible Issues (2)
History
Introduced in 1988 (1.0) | Updated in 2021 (13.0) ▪ 2022 (13.1)
Text
Wolfram Research (1988), Gamma, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Gamma.html (updated 2022).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 1988. "Gamma." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2022. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Gamma.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (1988). Gamma. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Gamma.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_gamma, author="Wolfram Research", title="{Gamma}", year="2022", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Gamma.html}", note=[Accessed: 28-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_gamma, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={Gamma}, year={2022}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Gamma.html}, note=[Accessed: 28-February-2026]}