GompertzMakehamDistribution[λ,ξ]
represents a Gompertz distribution with scale parameter λ and frailty parameter ξ.
GompertzMakehamDistribution[λ,ξ,θ,α]
represents a Gompertz–Makeham distribution with parameters λ, ξ, θ, and α.


GompertzMakehamDistribution
GompertzMakehamDistribution[λ,ξ]
represents a Gompertz distribution with scale parameter λ and frailty parameter ξ.
GompertzMakehamDistribution[λ,ξ,θ,α]
represents a Gompertz–Makeham distribution with parameters λ, ξ, θ, and α.
Details
- The hazard function for value
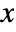 in a Gompertz distribution is given by
in a Gompertz distribution is given by 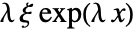 for
for 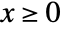 , and is zero for
, and is zero for 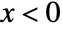 .
. - The hazard function for value
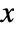 in a Gompertz–Makeham distribution is given by
in a Gompertz–Makeham distribution is given by 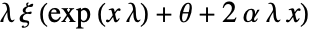 for
for 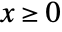 and is zero for
and is zero for 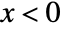 .
. - GompertzMakehamDistribution allows λ and ξ to be any positive real numbers and θ and α any non–negative real numbers.
- GompertzMakehamDistribution allows λ to be a quantity of any unit dimension and ξ, θ, and α to be dimensionless quantities. »
- GompertzMakehamDistribution can be used with such functions as Mean, CDF, and RandomVariate.
Background & Context
- GompertzMakehamDistribution[λ,ξ,θ,α] represents a continuous statistical distribution defined over the interval
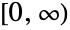 and parametrized by two non-negative real numbers θ and α and two positive real numbers λ and ξ called a "scale parameter" and a "frailty parameter", respectively. The overall behavior of the probability density function (PDF) of a Gompertz–Makeham distribution is determined by the values of the parameters λ, ξ, θ, and α, and in particular the PDF may be either monotonically decreasing with a potential singularity approaching the lower boundary of its domain or unimodal. In addition, depending on its parameters, the tails of the PDF may be either "fat" or "thin", in the sense that the PDF may decrease either algebraically or exponentially for large values of
and parametrized by two non-negative real numbers θ and α and two positive real numbers λ and ξ called a "scale parameter" and a "frailty parameter", respectively. The overall behavior of the probability density function (PDF) of a Gompertz–Makeham distribution is determined by the values of the parameters λ, ξ, θ, and α, and in particular the PDF may be either monotonically decreasing with a potential singularity approaching the lower boundary of its domain or unimodal. In addition, depending on its parameters, the tails of the PDF may be either "fat" or "thin", in the sense that the PDF may decrease either algebraically or exponentially for large values of 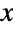 . (This behavior can be made quantitatively precise by analyzing the SurvivalFunction of the distribution.) The two-parameter version of the distribution GompertzMakehamDistribution[λ,ξ] is often referred to as the Gompertz distribution and is equivalent to GompertzMakehamDistribution[λ,ξ,0,0].
. (This behavior can be made quantitatively precise by analyzing the SurvivalFunction of the distribution.) The two-parameter version of the distribution GompertzMakehamDistribution[λ,ξ] is often referred to as the Gompertz distribution and is equivalent to GompertzMakehamDistribution[λ,ξ,0,0]. - The Gompertz–Makeham distribution was introduced in the 1890s when English mathematician W. M. Makeham generalized a distribution originally studied by British mathematician Benjamin Gompertz in the early 1820s. Gompertz's original distribution was constructed as an attempt to smoothly model human mortality, subject to the assumption that death is due only to deterioration, while Makeham's work was the result of generalizing this model to account for death stemming from either deterioration or random causes. The Gompertz–Makeham distribution is the basis for the so-called Gompertz–Makeham law of mortality, which states that the human death rate is composed of two components: one age dependent and the other age independent. This law is used in a number of fields, including computer science, actuarial science, gerontology, demography, biology, and reliability theory.
- RandomVariate can be used to give one or more machine- or arbitrary-precision (the latter via the WorkingPrecision option) pseudorandom variates from a Gompertz–Makeham distribution. Distributed[x,GompertzMakehamDistribution[λ,ξ,θ,α]], written more concisely as xGompertzMakehamDistribution[λ,ξ,θ,α], can be used to assert that a random variable x is distributed according to a Gompertz–Makeham distribution. Such an assertion can then be used in functions such as Probability, NProbability, Expectation, and NExpectation.
- The probability density and cumulative distribution functions may be given using PDF[GompertzMakehamDistribution[λ,ξ,θ,α],x] and CDF[GompertzMakehamDistribution[λ,ξ,θ,α],x]. The mean, median, variance, raw moments, and central moments may be computed using Mean, Median, Variance, Moment, and CentralMoment, respectively.
- DistributionFitTest can be used to test if a given dataset is consistent with a Gompertz–Makeham distribution, EstimatedDistribution to estimate a Gompertz–Makeham parametric distribution from given data, and FindDistributionParameters to fit data to a Gompertz–Makeham distribution. ProbabilityPlot can be used to generate a plot of the CDF of given data against the CDF of a symbolic Gompertz–Makeham distribution and QuantilePlot to generate a plot of the quantiles of given data against the quantiles of a symbolic Gompertz–Makeham distribution.
- TransformedDistribution can be used to represent a transformed Gompertz–Makeham distribution, CensoredDistribution to represent the distribution of values censored between upper and lower values, and TruncatedDistribution to represent the distribution of values truncated between upper and lower values. CopulaDistribution can be used to build higher-dimensional distributions that contain a Gompertz–Makeham distribution, and ProductDistribution can be used to compute a joint distribution with independent component distributions involving Gompertz–Makeham distributions.
- The Gompertz–Makeham distribution is related to several other distributions. For example, GompertzMakehamDistribution is related to ExponentialDistribution, in the sense that the hazard function (see HazardFunction) of GompertzMakehamDistribution[λ,θ/λ] tends to that of ExponentialDistribution[θ] as λ tends to zero. In addition, GompertzMakehamDistribution is a truncated GumbelDistribution (i.e. GumbelDistribution[a,b] restricted to [
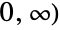 is the same as GompertzMakehamDistribution[1/b,Exp[-a/b]]). It is related to a truncated WeibullDistribution and therefore also to the other "extreme value distributions", namely to FrechetDistribution and to ExtremeValueDistribution. GompertzMakehamDistribution is also related to GammaDistribution, ExpGammaDistribution, RayleighDistribution, and StudentTDistribution.
is the same as GompertzMakehamDistribution[1/b,Exp[-a/b]]). It is related to a truncated WeibullDistribution and therefore also to the other "extreme value distributions", namely to FrechetDistribution and to ExtremeValueDistribution. GompertzMakehamDistribution is also related to GammaDistribution, ExpGammaDistribution, RayleighDistribution, and StudentTDistribution.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (6)
Scope (10)
Generate a sample of pseudorandom numbers from a Gompertz distribution:
Compare its histogram to the PDF:
Distribution parameters estimation:
Estimate the distribution parameters from sample data:
Compare the density histogram of the sample with the PDF of the estimated distribution:
Skewness of Gompertz distribution:
Kurtosis of Gompertz distribution:
Different moments of Gompertz distribution with closed forms as functions of parameters:
Hazard function of Gompertz distribution:
Hazard function of Gompertz–Makeham distribution:
Quantile function of Gompertz distribution:
Quantile function of Gompertz–Makeham distribution:
Consistent use of Quantity in parameters yields QuantityDistribution:
Applications (4)
The lifetime of a device has a Gompertz distribution. Find the reliability of the device:
The hazard function increasing in time:
Find the reliability of two such devices in series:
Find the reliability of two such devices in parallel:
Compare the reliability of both systems for ![]() and
and ![]() :
:
A steel pipe with thickness θ is exposed to corrosion and fails if any of the n microscopic pits penetrates the surface. Assume the time to penetration at each pit is proportional to the remaining thickness with factor k. If the depths of the pits are initially random and the depth in time follows a right-truncated exponential distribution with parameter λ, then time to failure of the pipe follows a Gompertz distribution. Find the reliability of the pipe:
Find the mean time to failure:
The female mortality in 1900 according to the Society of Actuaries is given by the table:
Create a sample population to use maximum likelihood estimation:
Fit Gompertz–Makeham distribution to the data:
Plot probability density function:
Compare the mortality data with the survival function of the estimated distribution:
Find the average female life length in 1900:
Compare the mean residual lifetime from the data with estimated distribution:
Define expo-power distribution using Gompertz distribution:
WeibullDistribution is a limiting case:
Properties & Relations (9)
GompertzMakehamDistribution is closed under scaling by a positive factor:
The family of Gompertz distributions is closed under a minimum:
For different frailty parameters:
The family of Gompertz–Makeham distributions is closed under a minimum:
For different frailty parameters:
Relationships to other distributions:
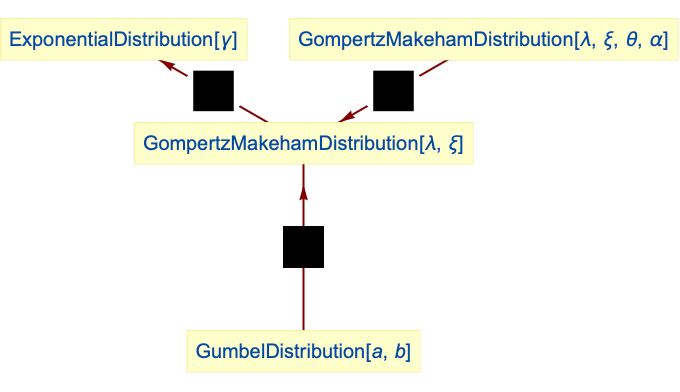
Gompertz distribution is related to exponential distribution:
The Gompertz–Makeham distribution simplifies to the Gompertz distribution for θ=0 and α=0:
Gompertz distribution is a truncated GumbelDistribution:
Gompertz distribution is related to truncated WeibullDistribution:
WeibullDistribution is related to Gompertz distribution:
See Also
Text
Wolfram Research (2010), GompertzMakehamDistribution, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/GompertzMakehamDistribution.html (updated 2016).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2010. "GompertzMakehamDistribution." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2016. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/GompertzMakehamDistribution.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2010). GompertzMakehamDistribution. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/GompertzMakehamDistribution.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_gompertzmakehamdistribution, author="Wolfram Research", title="{GompertzMakehamDistribution}", year="2016", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/GompertzMakehamDistribution.html}", note=[Accessed: 09-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_gompertzmakehamdistribution, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={GompertzMakehamDistribution}, year={2016}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/GompertzMakehamDistribution.html}, note=[Accessed: 09-March-2026]}