NonlinearStateSpaceModel[{f,g},x,u]
represents the model ![]() ,
, ![]() .
.
gives a state-space representation corresponding to the systems model sys.
NonlinearStateSpaceModel[eqns,{{x1,x10},…},{{u1,u10},…},{g1,…},t]
gives the state-space model of the differential equations eqns with dependent variables xi, input variables ui, operating values xi0 and ui0, outputs gi, and independent variable t.


NonlinearStateSpaceModel
NonlinearStateSpaceModel[{f,g},x,u]
represents the model ![]() ,
, ![]() .
.
gives a state-space representation corresponding to the systems model sys.
NonlinearStateSpaceModel[eqns,{{x1,x10},…},{{u1,u10},…},{g1,…},t]
gives the state-space model of the differential equations eqns with dependent variables xi, input variables ui, operating values xi0 and ui0, outputs gi, and independent variable t.
Details and Options


- NonlinearStateSpaceModel is a general representation state-space model.
- NonlinearStateSpaceModel[{f},x,u] assumes
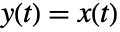 .
. - NonlinearStateSpaceModel[{f,g},x,u,y,t] explicitly specifies the output variables y and independent variable t.
- NonlinearStateSpaceModel allows for operating values for the states x and inputs u.
- NonlinearStateSpaceModel[…,{{x1,x10},…},{{u1,u10},…},…] is used to indicate the operating values for the system.
- In NonlinearStateSpaceModel[sys] the following systems can be converted:
-
AffineStateSpaceModel exact conversion StateSpaceModel exact conversion TransferFunctionModel exact conversion - In NonlinearStateSpaceModel[eqns,…] the Taylor linearization is with respect to the highest-order derivatives of
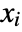 about the point
about the point 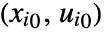 of the differential equations eqns.
of the differential equations eqns. - In computations where the operating point vi0 is Automatic, it is usually assumed to be zero.
- NonlinearStateSpaceModel[…]["prop"] gives the value of the property "prop".
- NonlinearStateSpaceModel[…]["Properties"] gives the list of available properties.
- The following options can be given:
-
Appearance Automatic model appearance ExternalTypeSignature Automatic variable types for embedded code SamplingPeriod Automatic sampling period SystemsModelLabels Automatic variable labels - The option Appearance can take values Automatic, "Detailed", "Structured", "Elided" and "Iconized".
- NonlinearStateSpaceModel can be used in functions such as OutputResponse and SystemsModelSeriesConnect.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (1)
Scope (23)
Basic Uses (5)
A system with 2 states ![]() , 1 input
, 1 input ![]() , and 1 output:
, and 1 output:
Count the number of inputs and outputs:
A system with 2 inputs and 1 output:
The response to a unit step applied to each input channel while holding the other at zero:
A system with 1 input and 2 outputs:
Connect the gains in series with the original system:
Specify operating values for the states:
Obtain the StateSpaceModel using linearization about the operating values:
System Conversions (4)
The nonlinear representation of a StateSpaceModel with specified states:
The nonlinear state-space representation of a TransferFunctionModel with default states:
The nonlinear representation of an AffineStateSpaceModel, preserving states:
Model Manipulations (3)
Set new state, input, and output variables:
Use state ![]() , input
, input ![]() , and output
, and output ![]() :
:
Use Normal to get the model's arguments:
Operating Values (6)
States and inputs deleted using SystemsModelDelete are set to their operating values:
So are the states and inputs not extracted by SystemsModelExtract:
StateSpaceTransform computes the operating values of the new states if the old were specified:
By default, the simulation functions assume the operating values as the initial values:
StateSpaceModel linearizes about all operating values:
AffineStateSpaceModel only linearizes about operating values of input variables:
NonlinearStateSpaceModel preserves operating values specified along with ODEs:
FullInformationOutputRegulator linearizes about the operating values to compute the gains ![]() :
:
Properties (5)
Options (3)
Applications (5)
Chemical Systems (2)
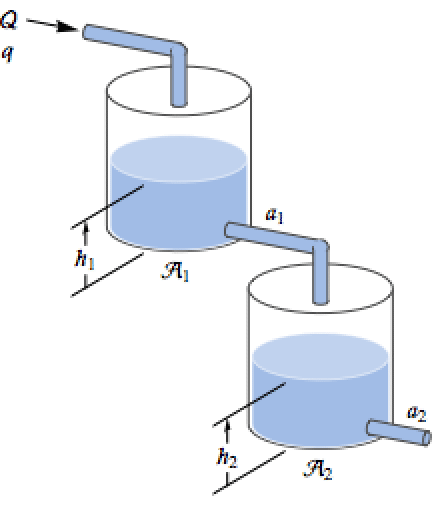
Use NonlinearStateSpaceModel to specify the equations for a two-tank system and simulate it:
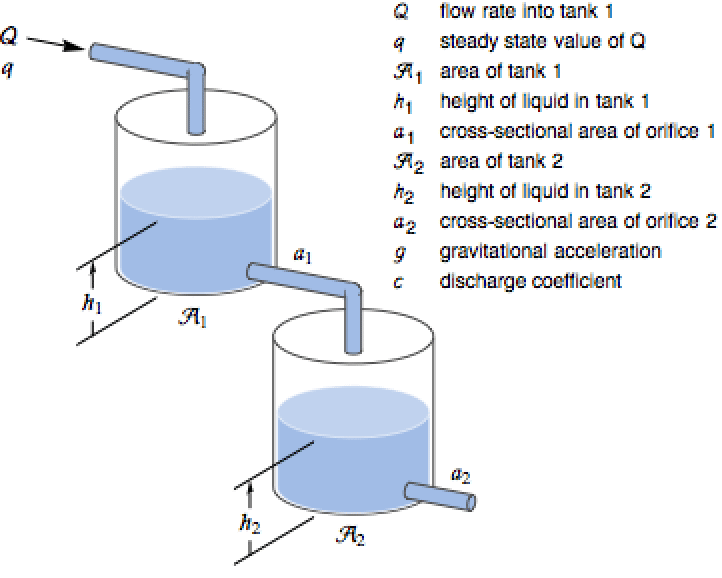
Use Bernoulli's law and mass balance to derive the resulting differential equations:
Use steady-state operating values ![]() :
:
Define the corresponding nonlinear system with input ![]() and output
and output ![]() :
:
With a higher steady-state value for flow rate, the level in the tanks settles at a higher level:
Control the level in the second tank below using a PID controller:
Obtain a PID controller using the linearized model and PIDTune:
Specify a piecewise reference value for the liquid level in the second tank:
The simulations show how the closed-loop system follows the reference:
Aerospace Systems (2)
Find the equations of motion of an aircraft's longitudinal dynamics ![]() , where the states
, where the states ![]() are
are ![]() and the inputs
and the inputs ![]() are
are ![]() : »
: »
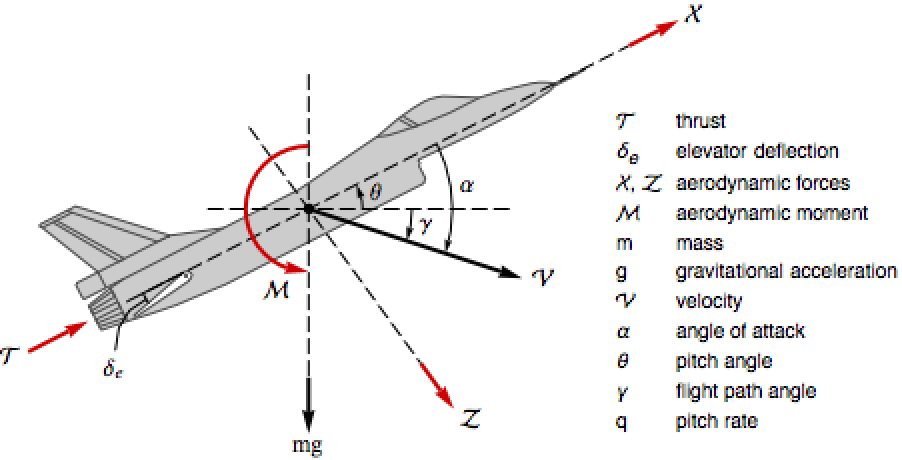
Here , , and ℳ are taken to be polynomials in α and δe:
The aerodynamic and model parameters:
Use ![]() , where
, where ![]() is the flight path angle and
is the flight path angle and ![]() the pitch angle:
the pitch angle:
Find the steady states for steady ![]() , level
, level ![]() flight at a specific speed
flight at a specific speed ![]() :
:
Define state variables and initial values:
The nonlinear state-space model of the aircraft with states ![]() and inputs
and inputs ![]() :
:
The 2×2 transfer function representation of the linearized system:
The system is unstable due to the poles in the right half-plane:
It is also nonminimum phase due to the zeros in the right half-plane:
The BodePlot shows that the velocity ![]() can be affected more than the flight path angle
can be affected more than the flight path angle ![]() :
:
The six-degree-of-freedom equations of motion of an aircraft. The rotation matrix for a rotation ![]() about an axis
about an axis ![]() : »
: »
The rotation matrices for the Euler angles ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() :
:
The matrix transformation of a vector from the body-fixed to the earth-fixed axes:
The inverse transformation from the earth-fixed to the body-fixed axes:
A figure showing the earth-fixed axes ![]() and body-fixed axes
and body-fixed axes ![]() :
:
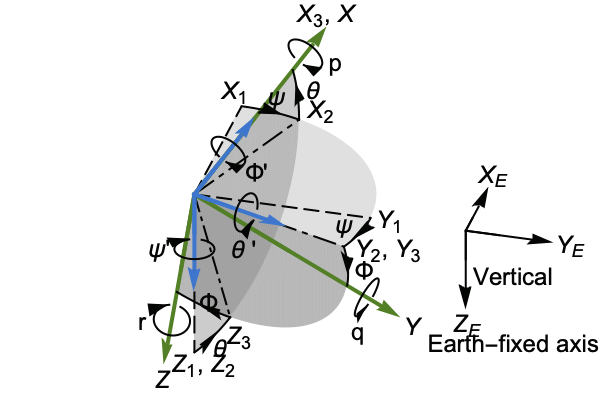
The Euler angle rates in terms of the angular velocity components ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() :
:
The kinematic equations for the Euler angles:
The kinematic equations for the flight path variables ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() :
:
The inertia matrix, assuming that the ![]() plane is a plane of symmetry:
plane is a plane of symmetry:
The angular momentum ![]() can be computed as
can be computed as ![]() :
:
A figure showing the forces and moments acting on the aircraft:
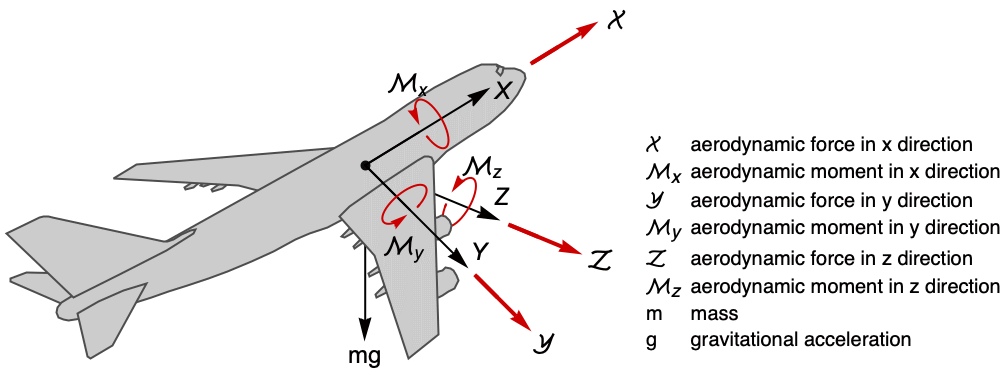
The state equations of the angular velocity can be obtained by solving the moment equation ![]() , where
, where ![]() is the vector of aerodynamic moments:
is the vector of aerodynamic moments:
The dynamics of the rotational motion:
The forces acting on the aircraft are the aerodynamic forces ![]() , its weight, and the thrust
, its weight, and the thrust ![]() :
:
The dynamics of the translational motion can be obtained from Newton's law ![]() :
:
The complete equations of motion for the aircraft:
The longitudinal dynamics are the dynamics for states ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() :
:
The lateral dynamics are the dynamics for the states ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() :
:
Extended Kalman Filter (1)
Design an extended Kalman filter to track the motion of a wheeled robot:
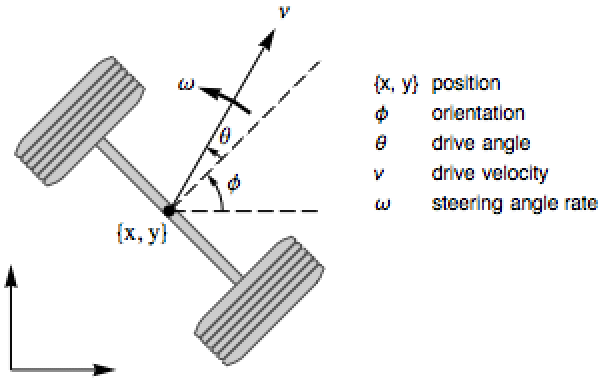
All the measurements are assumed to be noisy, with covariance ![]() :
:
The gain ![]() of the filter is based on the covariance
of the filter is based on the covariance ![]() of the states:
of the states:
The right-hand side of the differential equation for the estimated states with noisy measurements ![]() :
:
The right-hand side of the differential equation for the covariance matrix ![]() :
:
Assemble the estimator using NonlinearStateSpaceModel:
Simulate the robot from initial position ![]() and a set of inputs:
and a set of inputs:
Simulate the response of the filter using the inputs to the system and the noisy measurements:
Compare the actual, noisy, and filtered values of the variable ![]() :
:
Properties & Relations (3)
NonlinearStateSpaceModel converts to AffineStateSpaceModel by linearizing inputs:
Conversion the other way is exact:
NonlinearStateSpaceModel converts to StateSpaceModel by linearizing states and inputs:
Conversion the other way is exact:
Convert to TransferFunctionModel by state and input linearization:
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2014), NonlinearStateSpaceModel, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NonlinearStateSpaceModel.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2014. "NonlinearStateSpaceModel." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NonlinearStateSpaceModel.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2014). NonlinearStateSpaceModel. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NonlinearStateSpaceModel.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_nonlinearstatespacemodel, author="Wolfram Research", title="{NonlinearStateSpaceModel}", year="2014", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NonlinearStateSpaceModel.html}", note=[Accessed: 27-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_nonlinearstatespacemodel, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={NonlinearStateSpaceModel}, year={2014}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NonlinearStateSpaceModel.html}, note=[Accessed: 27-February-2026]}