SinDegrees[θ]
gives the sine of ![]() degrees.
degrees.




SinDegrees
SinDegrees[θ]
gives the sine of ![]() degrees.
degrees.
Details

- SinDegrees and other trigonometric functions are studied in high-school geometry courses and are also used in many scientific disciplines.
- The argument of SinDegrees is assumed to be in degrees.
- SinDegrees is automatically evaluated when its argument is a simple rational multiple of
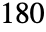 ; for more complicated rational multiples, FunctionExpand can sometimes be used.
; for more complicated rational multiples, FunctionExpand can sometimes be used. - SinDegrees of angle
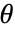 is the ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse of a right triangle:
is the ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse of a right triangle: - SinDegrees is related to CosDegrees by the Pythagorean identity
![TemplateBox[{theta}, SinDegrees]^2+TemplateBox[{theta}, CosDegrees]^2=1 TemplateBox[{theta}, SinDegrees]^2+TemplateBox[{theta}, CosDegrees]^2=1](Files/SinDegrees.en/4.png) .
. - For certain special arguments, SinDegrees automatically evaluates to exact values.
- SinDegrees can be evaluated to arbitrary numerical precision.
- SinDegrees automatically threads over lists.
- SinDegrees can be used with Interval, CenteredInterval and Around objects.
- Mathematical function, suitable for both symbolic and numerical manipulation.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (6)
The argument is given in degrees:
Calculate SinDegrees of 45 degrees for a right triangle with unit sides:
Solve a trigonometric equation:
Scope (47)
Numerical Evaluation (6)
The precision of the output tracks the precision of the input:
SinDegrees can take complex number inputs:
Evaluate SinDegrees efficiently at high precision:
Compute worst-case guaranteed intervals using Interval and CenteredInterval objects:
Or compute average-case statistical intervals using Around:
Compute the elementwise values of an array:
Or compute the matrix SinDegrees function using MatrixFunction:
Specific Values (6)
Values of SinDegrees at fixed points:
SinDegrees has exact values at rational multiples of 30 degrees:
Simple exact values are generated automatically:
More complicated cases require explicit use of FunctionExpand:
Zeros of SinDegrees:
Extrema of SinDegrees:
Visualization (4)
Plot the SinDegrees function:
Plot over a subset of the complexes:
Plot the real part of SinDegrees:
Plot the imaginary part of SinDegrees:
Polar plot with SinDegrees:
Function Properties (13)
SinDegrees is a periodic function with a period of 360 degrees:
Check this with FunctionPeriod:
SinDegrees is defined for all real and complex values:
SinDegrees achieves all real values between ![]() and
and ![]() :
:
The range for complex values is the whole plane:
SinDegrees is an odd function:
SinDegrees has the mirror property ![]() :
:
SinDegrees is an analytic function of x:
SinDegrees is monotonic in a specific range:
SinDegrees is not injective:
SinDegrees is not surjective:
SinDegrees is neither non-negative nor non-positive:
SinDegrees has no singularities or discontinuities:
SinDegrees is neither convex nor concave:
SinDegrees is concave for x in [0,180]:
TraditionalForm formatting:
Integration (3)
Compute the indefinite integral of SinDegrees via Integrate:
Definite integral of SinDegrees over a period is 0:
Series Expansions (3)
Find the Taylor expansion using Series:
Plots of the first three approximations for SinDegrees around ![]() :
:
SinDegrees can be applied to power series:
Function Identities and Simplifications (5)
Double-angle formula using TrigExpand:
Recover the original expression using TrigReduce:
Convert sums to products using TrigFactor:
Convert to exponentials using TrigToExp:
Function Representations (4)
Representation through CosDegrees:
Representations through CosDegrees, TanDegrees and CotDegrees:
Representation through CscDegrees:
Applications (22)
Basic Trigonometric Applications (3)
Given ![]() , find the SinDegrees of the angle
, find the SinDegrees of the angle ![]() :
:
Find the missing opposite side length of a right triangle with hypotenuse 5 given the angle is 30 degrees:
Trigonometric Identities (7)
Calculate the SinDegrees value of 105 degrees using the sum and difference formulas:
Compare with the result of direct calculation:
Calculate the SinDegrees value of 15 degrees using the half-angle formula ![]() :
:
Compare this result with directly calculated SinDegrees:
Calculate the product of two SinDegrees using the trigonometric product to sum formula ![]() :
:
Compare this result with directly calculated product of two SinDegrees instances:
Simplify trigonometric expressions:
Verify trigonometric identities:
Use the law of sines to find the length of the side ![]() opposite to the angle
opposite to the angle ![]() angle, given the length of the side
angle, given the length of the side ![]() and
and ![]() :
:
This could be calculated via the formula ![]() :
:
Calculate the base length of an isosceles triangle given the leg length ![]() and the vertex angle
and the vertex angle ![]() :
:
Trigonometric Equations (2)
Trigonometric Inequalities (2)
Advanced Applications (8)
Equiangular (logarithmic) spiral:
Approximate the almost nowhere differentiable Riemann–Weierstrass function:
Intensity of the Fraunhofer diffraction pattern of a circular aperture versus diffraction angle:
Find a point on a unit circle using CosDegrees and SinDegrees functions:
Properties & Relations (11)
Check that 1 degree is ![]() radians:
radians:
Basic parity and periodicity properties are automatically applied:
Complicated expressions containing trigonometric functions do not simplify automatically:
Use FunctionExpand to express SinDegrees in terms of radicals:
Compositions with the inverse trigonometric functions:
Solve a trigonometric equation:
Numerically find a root of a transcendental equation:
Plot the function to check if the solution is correct:
The zeros of SinDegrees:
FunctionExpand applied to SinDegrees generates expressions in trigonometric functions in radians:
ExpToTrig applied to the outputs of TrigToExp will generate trigonometric functions in radians:
SinDegrees is a numeric function:
Possible Issues (1)
See Also
CosDegrees TanDegrees CotDegrees CscDegrees ArcSinDegrees Sin
Tech Notes
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2024), SinDegrees, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/SinDegrees.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2024. "SinDegrees." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/SinDegrees.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2024). SinDegrees. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/SinDegrees.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_sindegrees, author="Wolfram Research", title="{SinDegrees}", year="2024", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/SinDegrees.html}", note=[Accessed: 10-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_sindegrees, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={SinDegrees}, year={2024}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/SinDegrees.html}, note=[Accessed: 10-March-2026]}