BesagL
BesagL[pdata,r]
estimates Besag's ![]() function
function ![]() for point data pdata at radius r.
for point data pdata at radius r.
BesagL[pproc,r]
computes ![]() for the point process pproc.
for the point process pproc.
BesagL[bdata,r]
computes ![]() for binned data bdata.
for binned data bdata.
BesagL[pspec]
generates the function ![]() that can be applied repeatedly to different radii r.
that can be applied repeatedly to different radii r.
Details and Options



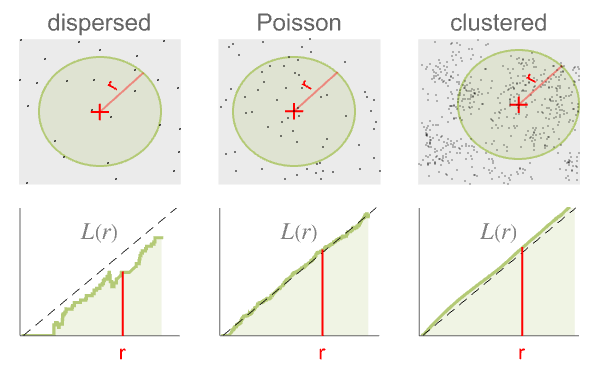
- BesagL is a transformation of the RipleyK function that makes it easier to compare to a completely spatially random reference process.
- BesagL
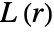 is defined as
is defined as 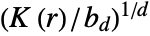 , where
, where 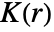 is RipleyK,
is RipleyK, 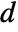 is the spatial dimension, and
is the spatial dimension, and 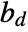 is the volume of a unit ball in
is the volume of a unit ball in 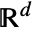 .
. -
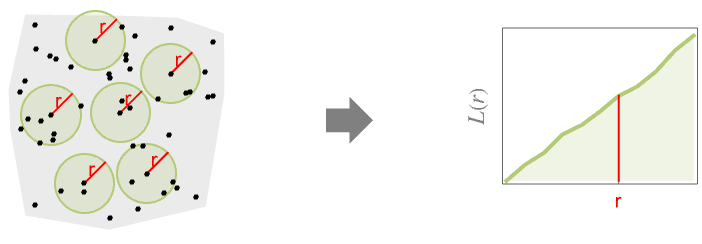
- BesagL measures spatial homogeneity of a point collection within distance r. Comparing with a Poisson point process gives:
-
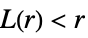
more dispersed than Poisson 
like Poisson, i.e. complete spatial randomness 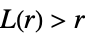
more clustered than Poisson -
- The radius r can be a single value or a list of values. With no radius r specified, BesagL returns a PointStatisticFunction that can be used to evaluate the
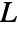 function repeatedly.
function repeatedly. - The points pdata can have the following forms:
-
{p1,p2,…} points pi GeoPosition[…],GeoPositionXYZ[…],… geographic points SpatialPointData[…] spatial point collection {pts,reg} point collection pts and observation region reg - If the observation region reg is not given, a region is automatically computed using RipleyRassonRegion.
- The point process pproc can have the following forms:
-
proc a point process proc {proc,reg} a point process proc and observation region reg - The observation region reg should be parameter free and SpatialObservationRegionQ.
- The binned data bdata is from SpatialBinnedPointData and is treated as an InhomogeneousPoissonPointProcess with a piecewise constant density function.
- For pdata,
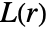 is computed by counting distinct pairs of points within distance r of each other.
is computed by counting distinct pairs of points within distance r of each other. - For pproc,
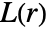 is computed by using exact formulas or by simulation to generate point data.
is computed by using exact formulas or by simulation to generate point data. - The following options can be given:
-
Method Automatic what methods to use SpatialBoundaryCorrection Automatic what boundary correction to use - The following settings can be used for SpatialBoundaryCorrection:
-
Automatic automatically determined boundary correction None no boundary correction "BorderMargin" use interior margin for observation region "Ripley" uses weights depending on the point distance to boundary
Examples
open allclose allBasic Examples (3)
Estimate Besag's ![]() function at a given distance:
function at a given distance:
Estimate Besag's ![]() function within a range of distances:
function within a range of distances:
Visualize the result with ListPlot:
Scope (10)
Point Data (5)
Estimate Besag's ![]() function at distance 0.2:
function at distance 0.2:
Obtain empirical estimates of Besag's ![]() function from a list of given distances:
function from a list of given distances:
Use BesagL with SpatialPointData:
Create a PointStatisticFunction for future use:
Estimate Besag's ![]() function without explicitly providing the observation region:
function without explicitly providing the observation region:
Observation region generated by Ripley–Rasson estimator:
Estimated ![]() function at distance 0.3:
function at distance 0.3:
Use BesagL with GeoPosition:
Point Processes (5)
Besag's ![]() function for PoissonPointProcess does not depend on the density or the dimension:
function for PoissonPointProcess does not depend on the density or the dimension:
Besag's ![]() function for a cluster process ThomasPointProcess with specified dimension:
function for a cluster process ThomasPointProcess with specified dimension:
Besag's ![]() function for a cluster process MaternPointProcess with specified dimension:
function for a cluster process MaternPointProcess with specified dimension:
Besag's ![]() function for a cluster process CauchyPointProcess:
function for a cluster process CauchyPointProcess:
Besag's ![]() function for a cluster process VarianceGammaPointProcess:
function for a cluster process VarianceGammaPointProcess:
Options (2)
SpatialBoundaryCorrection (2)
The BesagL estimator without boundary correction is biased and should not be used unless with a large point set:
The default method "BorderMargin" only considers the points that are distance ![]() from the boundary:
from the boundary:
Boundary correction method "Ripley" weights each pair of points to make the estimator unbiased:
Compare different edge correction methods:
Estimate the values of Besag's ![]() function with three different methods:
function with three different methods:
Applications (5)
Besag's ![]() function is cumulative in the distance and hence monotone increasing:
function is cumulative in the distance and hence monotone increasing:
Besag's ![]() function for complete spatial randomness:
function for complete spatial randomness:
Compute Besag's ![]() function for few dimensions:
function for few dimensions:
Points in a hardcore point process cannot be closer than the hard-core radius ![]() :
:
Estimate the values of Besag's ![]() function:
function:
Find hard-core radii estimates for the three samples:
Besag's ![]() of clustered data is higher than complete spatially random data. Sample from a cluster process:
of clustered data is higher than complete spatially random data. Sample from a cluster process:
Generate a control sample from a Poisson point process with the same intensity:
Compare the Besag's ![]() functions:
functions:
Use Besag's ![]() function to estimate PairCorrelationG:
function to estimate PairCorrelationG:
Compare the estimate with the pair correlation computed from the data:
Properties & Relations (1)
Text
Wolfram Research (2020), BesagL, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BesagL.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2020. "BesagL." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BesagL.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2020). BesagL. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BesagL.html