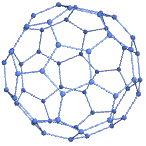
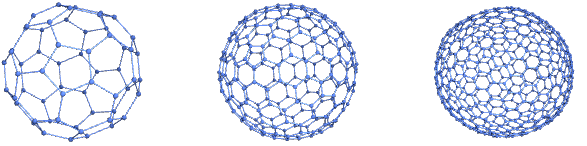
gives the buckyball graph.
gives the order‐n buckyball graph.
BuckyballGraph[n,"class"]
gives the order‐n buckyball graph of class "class".




BuckyballGraph
gives the buckyball graph.
gives the order‐n buckyball graph.
BuckyballGraph[n,"class"]
gives the order‐n buckyball graph of class "class".
Details and Options

- BuckyballGraph is also known as truncated icosahedral graph or fullerene graph.
- BuckyballGraph[] gives the 1-skeleton of the truncated icosahedron.
- BuckyballGraph[n,"I"] gives the 1-skeleton of the
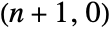 ‐Goldberg polyhedron.
‐Goldberg polyhedron. - BuckyballGraph[n,"II"] gives the 1-skeleton of the
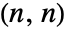 ‐Goldberg polyhedron.
‐Goldberg polyhedron. - BuckyballGraph[n] is effectively equivalent to BuckyballGraph[n,"II"].
- BuckyballGraph takes the same options as Graph3D.
-
AlignmentPoint Center the default point in the graphic to align with AnnotationRules {} annotations for graph, edges and vertices AspectRatio Automatic ratio of height to width Axes False whether to draw axes AxesEdge Automatic on which edges to put axes AxesLabel None axes labels AxesOrigin Automatic where axes should cross AxesStyle {} graphics directives to specify the style for axes Background None background color for the plot BaselinePosition Automatic how to align with a surrounding text baseline BaseStyle {} base style specifications for the graphic Boxed False whether to draw edges of the bounding box BoxRatios Automatic bounding 3D box ratios BoxStyle {} style specifications for the box ClipPlanes None clipping planes ClipPlanesStyle Automatic style specifications for clipping planes ContentSelectable Automatic whether to allow contents to be selected ControllerLinking False when to link to external rotation controllers ControllerPath Automatic what external controllers to try to use DirectedEdges Automatic whether to interpret Rule as DirectedEdge EdgeLabels Automatic labels and placements for edges EdgeLabelStyle Automatic style to use for edge labels EdgeShapeFunction Automatic generate graphic shapes for edges EdgeStyle Automatic styles for edges EdgeWeight Automatic weights for edges Epilog {} 2D graphics primitives to be rendered after the main plot FaceGrids None grid lines to draw on the bounding box FaceGridsStyle {} style specifications for face grids FormatType TraditionalForm default format type for text GraphHighlight {} graph elements to highlight GraphHighlightStyle Automatic style for highlight GraphLayout Automatic how to lay out vertices and edges ImageMargins 0. the margins to leave around the graphic ImagePadding All what extra padding to allow for labels, etc. ImageSize Automatic absolute size at which to render the graphic LabelStyle {} style specifications for labels Lighting Automatic simulated light sources to use Method Automatic details of 3D graphics methods to use PerformanceGoal Automatic aspects of performance to try to optimize PlotLabel None a label for the plot PlotRange All range of values to include PlotRangePadding Automatic how much to pad the range of values PlotRegion Automatic final display region to be filled PlotTheme Automatic overall style for graph elements PreserveImageOptions Automatic whether to preserve image options when displaying new versions of the same graphic Prolog {} 2D graphics primitives to be rendered before the main plot RotationAction "Fit" how to render after interactive rotation SphericalRegion Automatic whether to make the circumscribing sphere fit in the final display area Ticks Automatic specification for ticks TicksStyle {} style specification for ticks TouchscreenAutoZoom False whether to zoom to fullscreen when activated on a touchscreen VertexCoordinates Automatic coordinates for vertices VertexLabels Automatic labels and placements for vertices VertexLabelStyle Automatic style to use for vertex labels VertexShape Automatic graphic shape for vertices VertexShapeFunction Automatic generate graphic shapes for vertices VertexSize Medium size of vertices VertexStyle Automatic styles for vertices VertexWeight Automatic weights for vertices ViewAngle Automatic angle of the field of view ViewCenter Automatic point to display at the center ViewMatrix Automatic explicit transformation matrix ViewPoint {1.3,-2.4,2.} viewing position ViewProjection Automatic projection method for rendering objects distant from the viewer ViewRange All range of viewing distances to include ViewVector Automatic position and direction of a simulated camera ViewVertical {0,0,1} direction to make vertical
List of all options



Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Scope (4)
Options (77)
DirectedEdges (1)
By default, an undirected graph is generated:
Use DirectedEdges->True to generate a directed graph:
EdgeLabels (7)
Use any expression as a label:
Use Placed with symbolic locations to control label placement along an edge:
Use explicit coordinates to place labels:
Vary positions within the label:
Place multiple labels using Placed in a wrapper:
Any number of labels can be used:
Place multiple labels using EdgeLabels:
Use automatic labeling by values through Tooltip and StatusArea:
EdgeShapeFunction (6)
Get a list of built-in settings for EdgeShapeFunction:
Undirected edges including the basic line:
Lines with different glyphs on the edges:
Directed edges including solid arrows:
Specify an edge function for an individual edge:
Combine with a different default edge function:
Draw edges by running a program:
EdgeShapeFunction can be combined with EdgeStyle:
EdgeShapeFunction has higher priority than EdgeStyle:
EdgeStyle (4)
EdgeStyle can be combined with EdgeShapeFunction:
EdgeShapeFunction has higher priority than EdgeStyle:
EdgeWeight (3)
GraphLayout (5)
By default, the layout is chosen automatically:
Specify layouts on special curves:
Specify layouts that satisfy optimality criteria:
VertexCoordinates overrides GraphLayout coordinates:
Use AbsoluteOptions to extract VertexCoordinates computed using a layout algorithm:
PlotTheme (4)
VertexCoordinates (3)
By default, any vertex coordinates are computed automatically:
Extract the resulting vertex coordinates using AbsoluteOptions:
Specify a layout function along an ellipse:
Use it to generate vertex coordinates for a graph:
VertexCoordinates has higher priority than GraphLayout:
VertexLabels (13)
Use any expression as a label:
Use Placed with symbolic locations to control label placement, including outside positions:
Symbolic outside corner positions:
Symbolic inside corner positions:
Use explicit coordinates to place the center of labels:
Place all labels at the upper-right corner of the vertex and vary the coordinates within the label:
Any number of labels can be used:
Use the argument to Placed to control formatting including Tooltip:
Or StatusArea:
VertexShapeFunction (11)
Get a list of built-in collections for VertexShapeFunction:
Use built-in settings for VertexShapeFunction in the "Basic" collection:
Use built-in settings for VertexShapeFunction in the "Rounded" collection:
Use built-in settings for VertexShapeFunction in the "Concave" collection:
Combine with a default vertex function:
Draw vertices using a predefined graphic:
Draw vertices by running a program:
VertexShapeFunction can be combined with VertexStyle:
VertexShapeFunction has higher priority than VertexStyle:
VertexShapeFunction can be combined with VertexSize:
VertexShapeFunction has higher priority than VertexShape:
VertexSize (7)
By default, the size of vertices is computed automatically:
Specify the size of all vertices using symbolic vertex size:
Use a fraction of the minimum distance between vertex coordinates:
Use a fraction of the overall diagonal for all vertex coordinates:
Specify size in both the ![]() and
and ![]() directions:
directions:
Specify the size for individual vertices:
VertexSize can be combined with VertexShapeFunction:
VertexStyle (4)
VertexShapeFunction can be combined with VertexStyle:
VertexShapeFunction has higher priority than VertexStyle:
VertexStyle can be combined with BaseStyle:
VertexStyle has higher priority than BaseStyle:
Applications (11)
Basic Applications (7)
Style vertices and edges of a buckyball graph:
Annotate vertices and edges of a buckyball graph:
Modify a buckyball graph parameters:
Generate a buckyball graph represented as a 2D plot:
Basic properties of the class 1 buckyball graph; the number of vertices:
Basic properties of the class 2 buckyball graph; the number of vertices:
Graph Theory (4)
Properties & Relations (2)
The ratio of the number of vertices to the number of edges is ![]() :
:
BuckyballGraph[1] is the graph corresponding to the truncated icosahedron:
See Also
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2022), BuckyballGraph, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BuckyballGraph.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2022. "BuckyballGraph." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BuckyballGraph.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2022). BuckyballGraph. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BuckyballGraph.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_buckyballgraph, author="Wolfram Research", title="{BuckyballGraph}", year="2022", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BuckyballGraph.html}", note=[Accessed: 10-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_buckyballgraph, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={BuckyballGraph}, year={2022}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BuckyballGraph.html}, note=[Accessed: 10-March-2026]}