HypoexponentialDistribution[{λ1,…,λm}]
represents an m-phase hypoexponential distribution with rates λ1, …, λm.


HypoexponentialDistribution
HypoexponentialDistribution[{λ1,…,λm}]
represents an m-phase hypoexponential distribution with rates λ1, …, λm.
Details

- HypoexponentialDistribution is also known as a sequential m-phase exponential distribution.
- An m-phase hypoexponential distribution can be interpreted as having m servers in series where the i
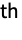 server has service rate λi.
server has service rate λi. - The probability density for value
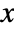 and distinct rates
and distinct rates 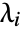 is a linear combination of exponentials
is a linear combination of exponentials 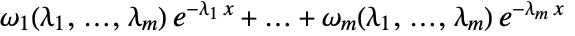 for
for 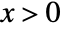 and zero for
and zero for 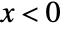 .
. - HypoexponentialDistribution[{λ1,…,λm}] is equivalent to TransformedDistribution[x1+⋯+xm,…] with each xi from ExponentialDistribution[λi].
- HypoexponentialDistribution allows λi to be any positive real numbers.
- HypoexponentialDistribution allows λi to be any quantities of the same unit dimensions. »
- HypoexponentialDistribution can be used with such functions as Mean, CDF, and RandomVariate.
Background & Context
- HypoexponentialDistribution[{λ1,…,λm}] represents a continuous statistical distribution defined over the interval
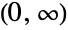 , parameterized by a vector (λ1,…,λm), and known as an
, parameterized by a vector (λ1,…,λm), and known as an 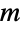 -phase hypoexponential distribution. The parameters λi are positive real values called "phase rates" and determine the overall shape of the probability density function (PDF), which in general is unimodal and has tails that are "thin" in the sense that the PDF decreases exponentially rather than decreasing algebraically for large values of
-phase hypoexponential distribution. The parameters λi are positive real values called "phase rates" and determine the overall shape of the probability density function (PDF), which in general is unimodal and has tails that are "thin" in the sense that the PDF decreases exponentially rather than decreasing algebraically for large values of 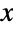 . (This behavior can be made quantitatively precise by analyzing the SurvivalFunction of the distribution.) Random variables X satisfying XHypoexponentialDistribution[{λ1,…,λm}] are said to have a hypoexponential distribution of order
. (This behavior can be made quantitatively precise by analyzing the SurvivalFunction of the distribution.) Random variables X satisfying XHypoexponentialDistribution[{λ1,…,λm}] are said to have a hypoexponential distribution of order 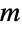 , and the hypoexponential distribution is sometimes referred to as the generalized Erlang distribution.
, and the hypoexponential distribution is sometimes referred to as the generalized Erlang distribution. - Named because its coefficient of variation (the ratio of StandardDeviation to Mean) is always smaller than 1 (which is the coefficient of variation for any exponential distribution), the hypoexponential distribution is an example of a mixture distribution (MixtureDistribution) and is often thought of as a generalization of ExponentialDistribution in the sense that its PDF models the distribution of a sum of exponentially distributed random variables. Because it has thin tails, the hypoexponential distribution is commonly used to study queueing systems. The hypoexponential distribution has also been used in the study of population genetics, manufacturing systems, reliability theory, and parallel computing.
- RandomVariate can be used to give one or more machine- or arbitrary-precision (the latter via the WorkingPrecision option) pseudorandom variates from a hypoexponential distribution. Distributed[x,HypoexponentialDistribution[{λ1,…,λm}] ], written more concisely as xHypoexponentialDistribution[{λ1,…,λm}] , can be used to assert that a random variable x is distributed according to a hypoexponential distribution. Such an assertion can then be used in functions such as Probability, NProbability, Expectation, and NExpectation.
- The probability density and cumulative distribution functions may be given using PDF[HypoexponentialDistribution[{λ1,…,λm}] ,x] and CDF[HypoexponentialDistribution[{λ1,…,λm}] ,x]. The mean, median, variance, raw moments, and central moments may be computed using Mean, Median, Variance, Moment, and CentralMoment, respectively.
- DistributionFitTest can be used to test if a given dataset is consistent with a hypoexponential distribution, EstimatedDistribution to estimate a hypoexponential parametric distribution from given data, and FindDistributionParameters to fit data to a hypoexponential distribution. ProbabilityPlot can be used to generate a plot of the CDF of given data against the CDF of a symbolic hypoexponential distribution, and QuantilePlot to generate a plot of the quantiles of given data against the quantiles of a symbolic hypoexponential distribution.
- TransformedDistribution can be used to represent a transformed hypoexponential distribution, CensoredDistribution to represent the distribution of values censored between upper and lower values, and TruncatedDistribution to represent the distribution of values truncated between upper and lower values. CopulaDistribution can be used to build higher-dimensional distributions that contain a hypoexponential distribution, and ProductDistribution can be used to compute a joint distribution with independent component distributions involving hypoexponential distributions.
- The hypoexponential distribution is related to a number of other distributions. HypoexponentialDistribution is an obvious generalization of ExponentialDistribution in that the PDF of HypoexponentialDistribution[{λ1,…,λm}] is precisely that of TransformedDistribution[x1+⋯+xm,{x1ExponentialDistribution[λ1],…,xmExponentialDistribution[λm]}], and an exponential distribution ExponentialDistribution[λ] can be viewed as a single-phase hypoexponential HypoexponentialDistribution[λ]. HypoexponentialDistribution has GammaDistribution and ErlangDistribution as special cases, is generalized by CoxianDistribution, and can be transformed into HyperexponentialDistribution (and vice versa). HypoexponentialDistribution can also be obtained from LaplaceDistribution, BenktanderWeibullDistribution, LogisticDistribution, ParetoDistribution, PearsonDistribution, PowerDistribution, and RayleighDistribution by composing transformations of ExponentialDistribution with TransformedDistribution and/or TruncatedDistribution, and is related to ExtremeValueDistribution, GumbelDistribution, FrechetDistribution, and WeibullDistribution, among others.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (4)
Scope (8)
Generate a sample of pseudorandom numbers from a hypoexponential distribution:
Compare the histogram to the PDF:
Distribution parameters estimation:
Estimate the distribution parameters from sample data:
Compare a density histogram of the sample with the PDF of the estimated distribution:
When both parameters go to ![]() simultaneously:
simultaneously:
When both parameters go to ![]() simultaneously:
simultaneously:
Different moments with closed forms as functions of parameters:
Closed form for symbolic order:
Consistent use of Quantity in parameters yields QuantityDistribution:
Applications (1)
A process is composed of three independent consecutive steps, each with mean time exponentially distributed with parameters 0.003 hr.![]() , .002 hr.
, .002 hr.![]() , and 0.01 hr.
, and 0.01 hr.![]() respectively. Find the probability that the process takes less than 500 hours:
respectively. Find the probability that the process takes less than 500 hours:
Find the mean duration of the process:
Find the median duration of the process:
Simulate the duration of the process in 50 consecutive runs:
Properties & Relations (11)
The variation coefficient of hypoexponential distribution is always less than the variation coefficient of ExponentialDistribution:
There are no valid parameters such that the variation coefficient of the hypoexponential distribution is greater than or equal to the variation coefficient of an exponential distribution:
Theoretically there is no limit on the length of the vector of ![]() s:
s:
Hypoexponential distribution is invariant under any permutation of the rates vector:
HypoexponentialDistribution is closed under addition:
HypoexponentialDistribution is closed under scaling by a positive factor:
Relationships to other distributions:
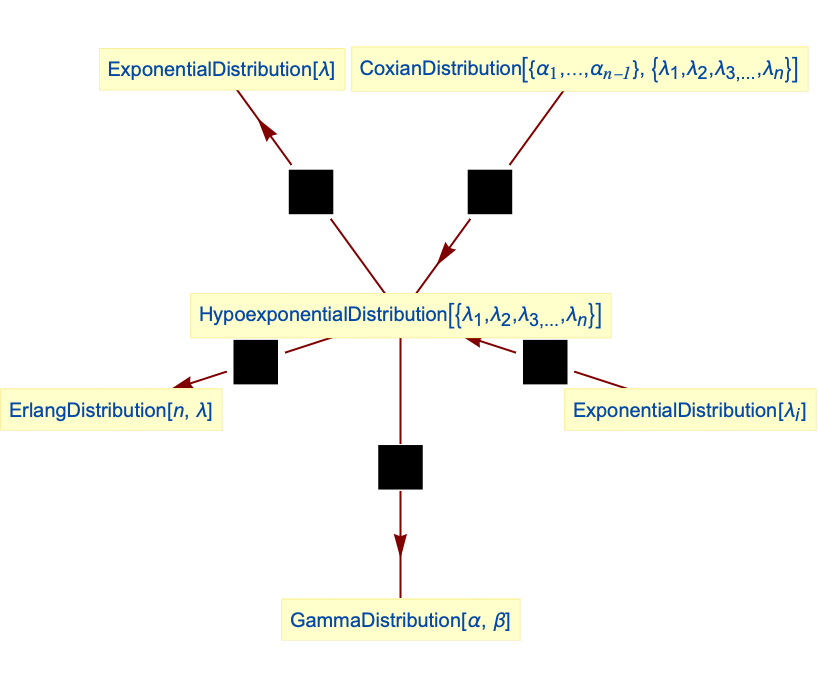
Sum of independent variables following ExponentialDistribution has hypoexponential distribution:
Hypoexponential distribution with single rate reduces to ExponentialDistribution:
HypoexponentialDistribution is a special case of CoxianDistribution:
Hypoexponential distribution with all rates equal is ErlangDistribution:
Hypoexponential distribution for all rates equal is GammaDistribution:
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2012), HypoexponentialDistribution, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HypoexponentialDistribution.html (updated 2016).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2012. "HypoexponentialDistribution." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2016. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HypoexponentialDistribution.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2012). HypoexponentialDistribution. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HypoexponentialDistribution.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_hypoexponentialdistribution, author="Wolfram Research", title="{HypoexponentialDistribution}", year="2016", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HypoexponentialDistribution.html}", note=[Accessed: 27-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_hypoexponentialdistribution, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={HypoexponentialDistribution}, year={2016}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HypoexponentialDistribution.html}, note=[Accessed: 27-February-2026]}