Inset[obj]
represents an object obj inset in a graphic.
Inset[obj,pos]
specifies that the inset should be placed at position pos in the graphic.
Inset[obj,pos,opos]
aligns the inset so that position opos in the object lies at position pos in the enclosing graphic.
Inset[obj,pos,opos,size]
specifies the size of the inset in the coordinate system of the enclosing graphic.
Inset[obj,pos,opos,size,dirs]
specifies that the axes of the inset should be oriented in directions dirs.


Inset
Inset[obj]
represents an object obj inset in a graphic.
Inset[obj,pos]
specifies that the inset should be placed at position pos in the graphic.
Inset[obj,pos,opos]
aligns the inset so that position opos in the object lies at position pos in the enclosing graphic.
Inset[obj,pos,opos,size]
specifies the size of the inset in the coordinate system of the enclosing graphic.
Inset[obj,pos,opos,size,dirs]
specifies that the axes of the inset should be oriented in directions dirs.
Details and Options
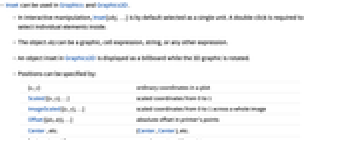




- Inset can be used in Graphics and Graphics3D.
- In interactive manipulation, Inset[obj,…] is by default selected as a single unit. A double‐click is required to select individual elements inside.
- The object obj can be a graphic, cell expression, string, or any other expression.
- An object inset in Graphics3D is displayed as a billboard while the 3D graphic is rotated.
- Positions can be specified by:
-
{x,y} ordinary coordinates in a plot Scaled[{x,y},…] scaled coordinates from 0 to 1 ImageScaled[{x,y},…] scaled coordinates from 0 to 1 across a whole image Offset[{dx,dy},…] absolute offset in printer's points Center, etc. {Center,Center}, etc. {valx,valy,valz} coordinates in a 3D graphic 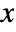 coordinates can be numbers, Automatic, or Left, Center, Right, or Axis.
coordinates can be numbers, Automatic, or Left, Center, Right, or Axis. 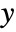 coordinates can be numbers, Automatic, or Top, Center, Bottom, Baseline, or Axis.
coordinates can be numbers, Automatic, or Top, Center, Bottom, Baseline, or Axis. - Axis corresponds to the position of the axis in a plot or the center line in typeset text.
- Center corresponds to a position centered with respect to the whole image.
- Inset[obj] is equivalent to Inset[obj,Center].
- The default for opos is the setting for the AlignmentPoint option of obj, or by default, the center of the bounding box for obj.
- If size is Automatic, the inset is given at its natural size:
-
graphic determined by ImageSize setting typeset expression absolute size without wrapping - A size of {w,Automatic} specifies that a typeset expression should be wrapped at width w.
- If size is given as {w,h}, then any object obj whose aspect ratio is not fixed will be horizontally or vertically stretched so as to fit exactly in a w×h rectangle.
- If obj is an object with fixed aspect ratio, then blank space will be left equally on both sides if there is a direction where the object would have to be stretched in order to fit exactly.
- The setting for the option Background specifies the background to be used for the whole region of the inset.
- By default, the inset is arranged so that its
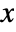 and
and 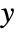 directions are oriented with the
directions are oriented with the 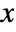 and
and 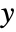 directions of the enclosing graphic.
directions of the enclosing graphic. - Inset[…,dirs] can be used to specify different orientations.
- Possible choices for dirs are:
-
Automatic default orientation {xx,xy} 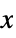 direction along {xx,xy}
direction along {xx,xy}{Automatic,{yx,yy}} 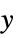 direction along {yx,yy}
direction along {yx,yy}{{xx,xy},{yx,yy}} 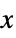 and
and 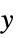 directions along {xx,xy} and {yx,yy}
directions along {xx,xy} and {yx,yy}None never reorient the contents of the Inset - Specifying only the
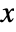 or only the
or only the 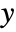 direction in general leads to a rigid rotation of the inset.
direction in general leads to a rigid rotation of the inset. - Specifying both the
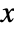 and
and 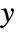 directions in general leads to a rotation and shear, in which the original inset rectangle becomes a parallelogram defined by the vector directions given.
directions in general leads to a rotation and shear, in which the original inset rectangle becomes a parallelogram defined by the vector directions given. - Only the directions of the vectors {xx,xy} and {yx,yy} are significant; the scale of the inset is determined by {w,h}.
- With dirs specified as None, the
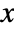 direction of obj is always maintained as horizontal.
direction of obj is always maintained as horizontal. - With dirs specified as {Automatic,None}, the
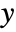 direction is maintained as vertical.
direction is maintained as vertical. - If Inset[Graphics3D[…],{x,y}] appears in a 2D graphic, then the projection of the alignment point of the Graphics3D, or by default the center of its 2D bounding box, will be placed at position {x,y} in the 2D graphic.
- Inset[Graphics3D[…],{x,y,z},{ox,oy}] specifies that position {ox,oy} in the 2D projection of the object should lie at position {x,y,z}.
- The 2D graphic is always taken to be oriented parallel to the viewing plane for the 3D graphic.
- The following options can be given for Inset:
-
Alignment Left how to align the contents of the inset Background None the background to use for the whole region of the inset BaseStyle {} the base style to use for the inset ContentSelectable Automatic whether to allow contents to be selected FormatType Automatic format type for text - Background->Automatic uses whatever background has been specified for the whole graphic containing the inset.
- Scaled, ImageScaled, and Offset forms can be used to specify the size.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (4)
Scope (19)
Positions (6)
Alignments (4)
Sizes (6)
If the size is not given, or is Automatic, the image size of the inset graphic is used:
For typeset expressions, absolute font size is used:
Specify the width of the inset by the units of the enclosing graphic:
Given both width and height sizes, the inset graphic will be stretched, if the aspect ratio is not fixed:
{w,Automatic} specifies the width at which a typeset expression should be wrapped:
In 3D graphics, image size is specified in absolute values:
Scaled can also be used to specify the image size:
Options (7)
FormatType (2)
By default, expressions are displayed using TraditionalForm:
Display expressions using StandardForm:
Applications (3)
Multiple function plot with a legend:
Set up an annotation function using Inset:
Display the map with the annotations:
Properties & Relations (2)
The symbolic positions are relative to ImageScaled coordinates:
For typeset expressions, Text offers functionality similar to Inset:
See Also
GraphicsGroup Item Graphics Graphics3D Locator Text Rectangle Pane Panel PlotMarkers ImageSizeAction Scale Rotate Magnify AttachCell
Function Repository: TessellateGraphics
Tech Notes
Related Workflows
- Inset One Graphic into Another
History
Introduced in 2007 (6.0) | Updated in 2008 (7.0) ▪ 2014 (10.0)
Text
Wolfram Research (2007), Inset, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Inset.html (updated 2014).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2007. "Inset." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2014. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Inset.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2007). Inset. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Inset.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_inset, author="Wolfram Research", title="{Inset}", year="2014", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Inset.html}", note=[Accessed: 12-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_inset, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={Inset}, year={2014}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Inset.html}, note=[Accessed: 12-March-2026]}