



Region
Details and Options

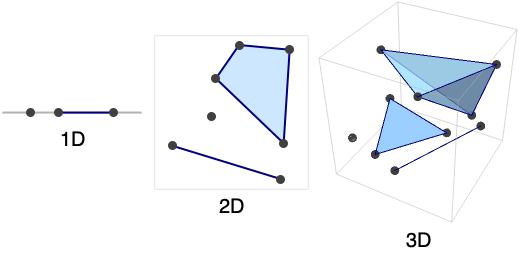
- Region[…] displays in a notebook as a plot of a region with embedding dimensions 1, 2 and 3.
- Region[reg,…] is always converted to an optimized standard form with structure Region[reg,data,…].
- Region has the same options as Graphics for embedding dimension 2 and the same options as Graphics3D for embedding dimension 3, with the following additions and changes:
-
PlotTheme $PlotTheme overall theme RegionSize Automatic print size of the region - Possible settings for PlotTheme include common base themes, font features themes and size features themes.
- Region can be used with functions such as RegionMember, RegionDistance, RegionMeasure and NIntegrate.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (3)
A MeshRegion is a Region with an additional mesh structure:
Region represents the underlying three-dimensional point set without the mesh structure:
Style a Region:
Scope (35)
Regions (14)
Regions in 1D (3)
Regions in 2D (5)
A strictly 0D Region is a point set:
A strictly 1D Region is a collection of line segments:
A strictly 2D Region is a collection of polygonal faces:
A Region can combine elements of different dimensions:
Polygons with GeoGridPosition:
Regions in 3D (6)
A strictly 0D Region is a point set:
A strictly 1D Region is a collection of line segments:
A strictly 2D Region is a collection of polygonal faces:
A strictly 3D Region is a collection of polyhedral volumes:
Polyhedral volume cells include Cone, Cuboid, Pyramid etc.:
A Region can combine elements of different dimensions:
PolygonCoordinates works on polygons of geographic entities:
Polygons with GeoPosition:
Polygons with GeoPositionXYZ:
Polygons with GeoPositionENU:
Presentation (8)
Properties (8)
Wrappers (5)
Use wrappers on a Region:
Add interactive behavior with wrappers such as Tooltip:
Any object can be used in the tooltip:
Use Button to trigger actions when clicking a Region:
Use PopupWindow to provide information drilldown:
Options (96)
AlignmentPoint (1)
Specify the position to be aligned in 3D Inset, using ![]() coordinates:
coordinates:
AspectRatio (1)
Use numerical values for AspectRatio:
AxesEdge (2)
AxesStyle (2)
BaselinePosition (3)
Align the center of a graphic with the baseline of the text:
Specify the baseline of a graphic as a fraction of the height by using Scaled:
BoxRatios (2)
FaceGrids (4)
FrameTicks (3)
FrameTicksStyle (2)
GridLines (3)
ImageMargins (3)
Allow no margins outside of ImageSize:
ImagePadding (4)
ImageSize (3)
Lighting (4)
PlotLabel (2)
Display a label on the top of the graphic in TraditionalForm:
Use Style and other typesetting functions to modify how the label appears:
PlotRange (3)
PlotRangeClipping (2)
PlotRangePadding (3)
Include 1 coordinate unit of padding on all sides:
Include padding using Scaled coordinates:
PlotRegion (3)
The contents of a graphic use the whole region:
Limit the contents of the graphic to the middle half of the region in each direction:
ImagePadding can also be used to add padding around a graphic:
PlotTheme (3)
RotateLabel (2)
SphericalRegion (2)
Make a sequence of images be consistently sized, independent of orientation:
Without SphericalRegion, each image is made as big as possible:
Ticks (3)
TicksStyle (2)
ViewPoint (3)
ViewRange (2)
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2017), Region, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Region.html (updated 2017).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2017. "Region." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2017. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Region.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2017). Region. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Region.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_region, author="Wolfram Research", title="{Region}", year="2017", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Region.html}", note=[Accessed: 10-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_region, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={Region}, year={2017}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Region.html}, note=[Accessed: 10-March-2026]}