TreePlot[g]
generates a tree plot of the graph g.
TreePlot[{e1,e2,…}]
generates a tree plot of the graph with edges ej.
TreePlot[{…,w[ei],…}]
plots ei with features defined by the symbolic wrapper w.
TreePlot[{vi 1vj 1,…}]
uses rules vi 1vj 1 to specify the graph g.
TreePlot[m]
generates a tree plot of the graph represented by the adjacency matrix m.
TreePlot[…,vpos]
places the root v in the plot at position pos.




TreePlot
TreePlot[g]
generates a tree plot of the graph g.
TreePlot[{e1,e2,…}]
generates a tree plot of the graph with edges ej.
TreePlot[{…,w[ei],…}]
plots ei with features defined by the symbolic wrapper w.
TreePlot[{vi 1vj 1,…}]
uses rules vi 1vj 1 to specify the graph g.
TreePlot[m]
generates a tree plot of the graph represented by the adjacency matrix m.
TreePlot[…,vpos]
places the root v in the plot at position pos.
Details and Options


- TreePlot is also known as tree diagram.
- TreePlot attempts to place vertices in a tree of successive layers, or a collection of trees.
- TreePlot supports the same vertices and edges as Graph.
- If the graph g is not a tree, TreePlot lays out its vertices on the basis of a spanning tree of each connected component of the graph.
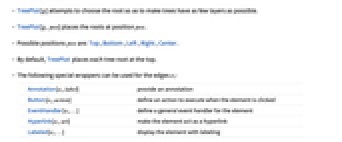
- TreePlot[g] attempts to choose the root so as to make trees have as few layers as possible.
- TreePlot[g,pos] places the roots at position pos.
- Possible positions pos are: Top, Bottom, Left, Right, Center.
- By default, TreePlot places each tree root at the top.
- The following special wrappers can be used for the edges ei:
-
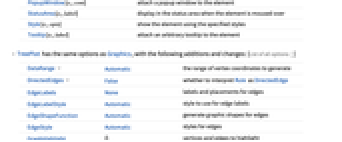
Annotation[ei,label] provide an annotation Button[ei,action] define an action to execute when the element is clicked EventHandler[ei,…] define a general event handler for the element Hyperlink[ei,uri] make the element act as a hyperlink Labeled[ei,…] display the element with labeling PopupWindow[ei,cont] attach a popup window to the element StatusArea[ei,label] display in the status area when the element is moused over Style[ei,opts] show the element using the specified styles Tooltip[ei,label] attach an arbitrary tooltip to the element - TreePlot has the same options as Graphics, with the following additions and changes: [List of all options]
-
DataRange Automatic the range of vertex coordinates to generate DirectedEdges False whether to interpret Rule as DirectedEdge EdgeLabels None labels and placements for edges EdgeLabelStyle Automatic style to use for edge labels EdgeShapeFunction Automatic generate graphic shapes for edges EdgeStyle Automatic styles for edges GraphHighlight {} vertices and edges to highlight GraphHighlightStyle Automatic style for highlight LayerSizeFunction (1) the height to allow for each layer PerformanceGoal Automatic aspects of performance to try to optimize PlotStyle Automatic graphics directives to determine styles PlotTheme Automatic overall theme for the graph VertexCoordinates Automatic coordinates for vertices VertexLabels None labels and placements for vertices VertexLabelStyle Automatic style to use for vertex labels VertexShape Automatic graphic shape for vertices VertexShapeFunction Automatic generate graphic shapes for vertices VertexSize Automatic size of vertices VertexStyle Automatic styles for vertices - Possible settings for PlotTheme include common base themes:
-
"Business" a bright, modern look appropriate for business presentations or infographics 
"Detailed" identify data by employing labels and tooltips 
"Marketing" elegant, eye-catching design suitable for marketing needs 
"Minimal" simple graph 
"Monochrome" single-color design 
"Scientific" candid design useful for analyzing detailed data with labels and tooltips 
"Web" clean, bold design suitable for a consumer website or blog 
"Classic" historical design of graph to remain compatible with existing uses - Graph feature themes affect the plots of vertices and edges. Feature themes include:
-
"LargeGraph" large graph 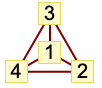
"ClassicLabeled" classic graph 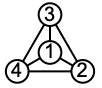
"IndexLabeled" index-labeled graph -
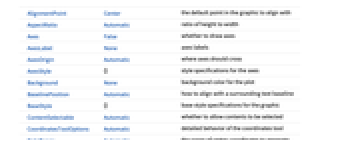
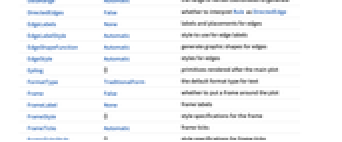
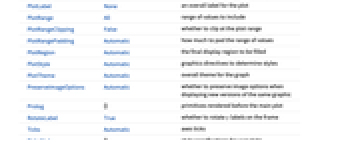
AlignmentPoint Center the default point in the graphic to align with AspectRatio Automatic ratio of height to width Axes False whether to draw axes AxesLabel None axes labels AxesOrigin Automatic where axes should cross AxesStyle {} style specifications for the axes Background None background color for the plot BaselinePosition Automatic how to align with a surrounding text baseline BaseStyle {} base style specifications for the graphic ContentSelectable Automatic whether to allow contents to be selected CoordinatesToolOptions Automatic detailed behavior of the coordinates tool DataRange Automatic the range of vertex coordinates to generate DirectedEdges False whether to interpret Rule as DirectedEdge EdgeLabels None labels and placements for edges EdgeLabelStyle Automatic style to use for edge labels EdgeShapeFunction Automatic generate graphic shapes for edges EdgeStyle Automatic styles for edges Epilog {} primitives rendered after the main plot FormatType TraditionalForm the default format type for text Frame False whether to put a frame around the plot FrameLabel None frame labels FrameStyle {} style specifications for the frame FrameTicks Automatic frame ticks FrameTicksStyle {} style specifications for frame ticks GraphHighlight {} vertices and edges to highlight GraphHighlightStyle Automatic style for highlight GridLines None grid lines to draw GridLinesStyle {} style specifications for grid lines ImageMargins 0. the margins to leave around the graphic ImagePadding All what extra padding to allow for labels etc. ImageSize Automatic the absolute size at which to render the graphic LabelStyle {} style specifications for labels LayerSizeFunction (1) the height to allow for each layer Method Automatic details of graphics methods to use PerformanceGoal Automatic aspects of performance to try to optimize PlotLabel None an overall label for the plot PlotRange All range of values to include PlotRangeClipping False whether to clip at the plot range PlotRangePadding Automatic how much to pad the range of values PlotRegion Automatic the final display region to be filled PlotStyle Automatic graphics directives to determine styles PlotTheme Automatic overall theme for the graph PreserveImageOptions Automatic whether to preserve image options when displaying new versions of the same graphic Prolog {} primitives rendered before the main plot RotateLabel True whether to rotate y labels on the frame Ticks Automatic axes ticks TicksStyle {} style specifications for axes ticks VertexCoordinates Automatic coordinates for vertices VertexLabels None labels and placements for vertices VertexLabelStyle Automatic style to use for vertex labels VertexShape Automatic graphic shape for vertices VertexShapeFunction Automatic generate graphic shapes for vertices VertexSize Automatic size of vertices VertexStyle Automatic styles for vertices
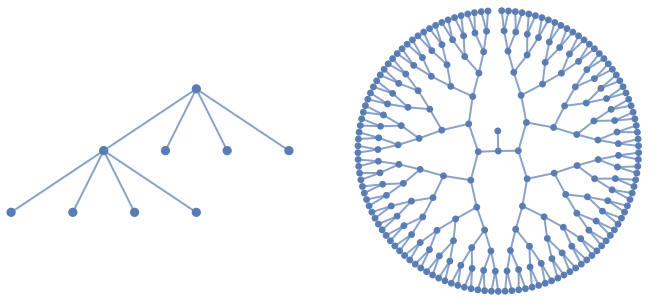
List of all options


Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (5)
Scope (10)
Graph Specification (4)
Options (35)
AspectRatio (1)
By default, the ratio of the height to width for the plot is determined automatically:
AspectRatio1 will make width equal to height:
AspectRatioFull adjusts the height and width to tightly fit inside other constructs:
Axes (1)
AxesOrigin (2)
AxesStyle (4)
Frame (4)
FrameLabel (4)
ImageSize (7)
Use named sizes such as Tiny, Small, Medium and Large:
Specify the width of the plot:
Specify the height of the plot:
Allow the width and height to be up to a certain size:
Specify the width and height for a graphic, padding with space if necessary:
Setting AspectRatioFull will fill the available space:
Use maximum sizes for the width and height:
Use ImageSizeFull to fill the available space in an object:
Specify the image size as a fraction of the available space:
LayerSizeFunction (2)
PlotStyle (3)
Specify an overall style for the graph:
PlotStyle can be combined with VertexShapeFunction, which has higher priority:
PlotStyle can be combined with EdgeShapeFunction, which has higher priority:
Applications (8)
Properties & Relations (4)
If the graph is not a tree, it is laid out based on a spanning tree of this graph:
Use LayeredGraphPlot for hierarchical-style drawing of a directed graph:
Use GraphPlot or GraphPlot3D for general undirected graph drawing:
Use ArrayPlot or MatrixPlot to display sparse matrices:
Possible Issues (2)
For nontree graphs, edges may overlap:
Use LayeredGraphPlot or GraphPlot to avoid overlapping edges:
TreePlot automatically chooses the base node to minimize tree height:
Explicitly specify a top node, which in this case is also the root node:
See Also
TreeGraph Graph LayeredGraphPlot GraphPlot TreeForm CommunityGraphPlot GraphLayout GraphEmbedding
Function Repository: GenealogyTreePlot
Text
Wolfram Research (2007), TreePlot, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/TreePlot.html (updated 2020).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2007. "TreePlot." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2020. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/TreePlot.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2007). TreePlot. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/TreePlot.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_treeplot, author="Wolfram Research", title="{TreePlot}", year="2020", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/TreePlot.html}", note=[Accessed: 16-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_treeplot, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={TreePlot}, year={2020}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/TreePlot.html}, note=[Accessed: 16-February-2026]}