ArrayPlot[array]
generates a plot in which the values in an array are shown in a discrete array of squares.




ArrayPlot
ArrayPlot[array]
generates a plot in which the values in an array are shown in a discrete array of squares.
Details and Options
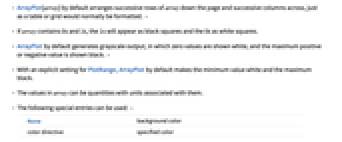




- ArrayPlot[array] by default arranges successive rows of array down the page and successive columns across, just as a table or grid would normally be formatted. »
- If array contains 0s and 1s, the 1s will appear as black squares and the 0s as white squares.
- ArrayPlot by default generates grayscale output, in which zero values are shown white, and the maximum positive or negative value is shown black. »
- With an explicit setting for PlotRange, ArrayPlot by default makes the minimum value white and the maximum black.
- The values in array can be quantities with units associated with them.
- The following special entries can be used: »
-
None background color color directive specified color - If array is ragged, shorter rows are treated as padded on the right with background. »
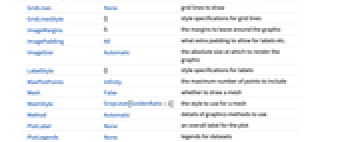
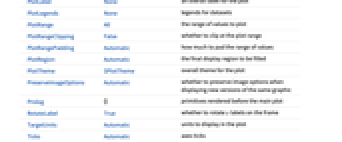
- ArrayPlot has the same options as Graphics, with the following additions and changes: [List of all options]
-
AspectRatio Automatic ratio of height to width ClippingStyle None how to show cells whose values are clipped ColorFunction Automatic how each cell should be colored ColorFunctionScaling True whether to scale the argument to ColorFunction ColorRules Automatic rules for determining colors from values DataRange All the range of 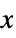 and
and 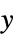 values to assume
values to assume DataReversed False whether to reverse the order of rows Frame Automatic whether to draw a frame around the plot FrameLabel None labels for rows and columns FrameTicks None what ticks to include on the frame MaxPlotPoints Infinity the maximum number of points to include Mesh False whether to draw a mesh MeshStyle GrayLevel[GoldenRatio-1] the style to use for a mesh PlotLegends None legends for datasets PlotRange All the range of values to plot PlotTheme $PlotTheme overall theme for the plot TargetUnits Automatic units to display in the plot - ColorRules can take the following settings:
-
Automatic use default colors "Colors" use colors for different values "Monochrome" use grayscale colors {valcolor,…} use color as the style for val - The rules given by ColorRules are applied to the value
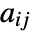 of each cell. The rules can involve patterns. »
of each cell. The rules can involve patterns. » - If none of the rules in ColorRules apply, then ColorFunction is used to determine the color.
- With the default setting ColorRules->Automatic, an explicit setting ColorFunction->f is used instead of ColorRules.
- With ColorFunctionScaling->False, each value
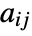 is supplied as the argument to any function given for ColorFunction. »
is supplied as the argument to any function given for ColorFunction. » - With ColorFunctionScaling->True, the values are scaled to lie between 0 and 1. »
- If the color determined for a particular cell is None, the cell is rendered in the background color.
- If no color is determined for a particular cell, the cell is rendered in a default dark red color.
- With DataReversed->True, the order of rows is reversed, so that rows run from bottom to top, with the last row at the top.
- With the setting FrameTicks->Automatic, ticks are placed at round integers, typically multiples of 5 or 10.
- With the setting FrameTicks->All, ticks are also placed at the minimum and maximum
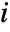 and
and 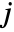 .
. - In explicit FrameTicks specifications, the tick coordinates are taken to refer to
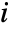 and
and 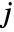 .
. - With DataReversed->True, tick values decrease from top to bottom.
- PlotRange->amax specifies that only those
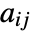 between 0 and amax should be shown. »
between 0 and amax should be shown. » - PlotRange->{amin,amax} specifies that
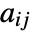 between amin and amax should be shown.
between amin and amax should be shown. - PlotRange->{{imin,imax},{jmin,jmax}} shows only elements with
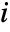 and
and 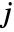 in the specified ranges. The top‐left element has
in the specified ranges. The top‐left element has 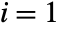 ,
, 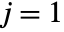 . With the default setting DataReversed->False,
. With the default setting DataReversed->False, 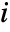 increases down the page;
increases down the page; 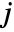 increases to the right.
increases to the right. - PlotRange->{ispec,jspec,aspec} shows only elements in the specified ranges of
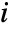 ,
, 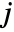 , and value. »
, and value. » - With the default setting for ColorFunction, PlotRange->{amin,amax} specifies that values from amin to amax should be shown with gray scales varying from white to black.
- Possible settings for Mesh include:
-
False do not draw any mesh lines True draw mesh lines between all cells Automatic draw mesh lines around original cells only "Nonzero" draw mesh lines around nonzero cells {mi,mj} use mesh specifications for the i and j directions - With the default setting Frame->Automatic, a frame is drawn only when Mesh->False.
- For purposes of combining with other graphics, the array element
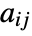 is taken to cover a unit square centered at coordinate position
is taken to cover a unit square centered at coordinate position 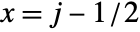 ,
, 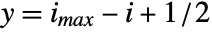 .
. - A setting DataRange->{{xmin,xmax},{ymin,ymax}} specifies that the centers of successive cells should be at equally spaced positions between xmin and xmax in the horizontal direction, and ymin and ymax in the vertical direction. With the default setting DataReversed->False,
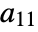 is centered at {xmin,ymax}.
is centered at {xmin,ymax}. - With the default setting DataRange->All and DataReversed->False, the array element
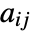 will be taken to cover a unit square centered at coordinate position
will be taken to cover a unit square centered at coordinate position 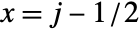 ,
, 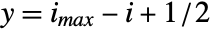 .
. - ArrayPlot returns Graphics[Raster[data],opts].
- ArrayPlot works with SparseArray objects. »
-
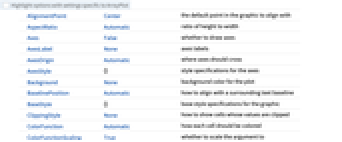
AlignmentPoint Center the default point in the graphic to align with AspectRatio Automatic ratio of height to width Axes False whether to draw axes AxesLabel None axes labels AxesOrigin Automatic where axes should cross AxesStyle {} style specifications for the axes Background None background color for the plot BaselinePosition Automatic how to align with a surrounding text baseline BaseStyle {} base style specifications for the graphic ClippingStyle None how to show cells whose values are clipped ColorFunction Automatic how each cell should be colored ColorFunctionScaling True whether to scale the argument to ColorFunction ColorRules Automatic rules for determining colors from values ContentSelectable Automatic whether to allow contents to be selected CoordinatesToolOptions Automatic detailed behavior of the coordinates tool DataRange All the range of 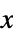 and
and 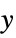 values to assume
values to assume DataReversed False whether to reverse the order of rows Epilog {} primitives rendered after the main plot FormatType TraditionalForm the default format type for text Frame Automatic whether to draw a frame around the plot FrameLabel None labels for rows and columns FrameStyle {} style specifications for the frame FrameTicks None what ticks to include on the frame FrameTicksStyle {} style specifications for frame ticks GridLines None grid lines to draw GridLinesStyle {} style specifications for grid lines ImageMargins 0. the margins to leave around the graphic ImagePadding All what extra padding to allow for labels etc. ImageSize Automatic the absolute size at which to render the graphic LabelStyle {} style specifications for labels MaxPlotPoints Infinity the maximum number of points to include Mesh False whether to draw a mesh MeshStyle GrayLevel[GoldenRatio-1] the style to use for a mesh Method Automatic details of graphics methods to use PlotLabel None an overall label for the plot PlotLegends None legends for datasets PlotRange All the range of values to plot PlotRangeClipping False whether to clip at the plot range PlotRangePadding Automatic how much to pad the range of values PlotRegion Automatic the final display region to be filled PlotTheme $PlotTheme overall theme for the plot PreserveImageOptions Automatic whether to preserve image options when displaying new versions of the same graphic Prolog {} primitives rendered before the main plot RotateLabel True whether to rotate y labels on the frame TargetUnits Automatic units to display in the plot Ticks Automatic axes ticks TicksStyle {} style specifications for axes ticks
List of all options

Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (6)
Scope (7)
By default, absolute values go from white to black:
Unknown or symbolic values are shown dark red:
Specify explicit colors for each cell:
Plot a ragged array, padding on the right:
Cells with value None are rendered like the background:
Options (96)
Axes (4)
By default, ArrayPlot uses a frame instead of axes:
Use AxesOrigin to specify where the axes intersect:
AxesOrigin (2)
AxesStyle (4)
Background (4)
Background is normally visible only around the edges:
The background "shows through" whenever an explicit entry is None:
Background also by default shows through for values outside the plot range:
ClippingStyle overrides background color:
ClippingStyle (3)
ColorFunction (5)
Map values from 0 to 1 onto colors according to Hue:
Use a pure function as the color function:
Use a named color gradient from ColorData:
Show elements with value 1 as black and all others as white:
With ColorFunctionScaling->True, the values are first scaled to lie between 0 and 1:
ColorRules (6)
Specify color rules for explicit values or patterns:
ColorFunction is used if no color rules apply:
The array can contain symbolic values:
Implement a "default color" by adding a rule for _:
Use any patterns in ColorRules:
DataReversed (4)
Epilog (3)
Frame (4)
FrameLabel (3)
FrameTicks (13)
Frame ticks are not included by default:
Use frame ticks on the bottom edge:
By default, none of the edges have either tick marks or tick labels:
Use automatic tick placements to include tick labels on all edges:
Use FrameTicksAll to include tick labels on all edges:
Place tick marks at specific positions:
Draw frame tick marks at the specified positions with specific labels:
Specify the lengths for tick marks as a fraction of the graphics size:
Use different sizes in the positive and negative directions for each tick mark:
Specify a style for each frame tick:
Construct a function that places frame ticks at the midpoint and extremes of the frame edge:
Frame ticks without a visible frame:
With a mesh included, Frame->True is required for frame ticks to be drawn:
FrameTicksStyle (3)
GridLines (3)
ImageSize (7)
Use named sizes such as Tiny, Small, Medium and Large:
Specify the width of the plot:
Specify the height of the plot:
Allow the width and height to be up to a certain size:
Specify the width and height for a graphic, padding with space if necessary:
Setting AspectRatioFull will fill the available space:
Use maximum sizes for the width and height:
Use ImageSizeFull to fill the available space in an object:
Specify the image size as a fraction of the available space:
MaxPlotPoints (1)
Use MaxPlotPoints to limit the number of elements explicitly plotted in each direction:
Mesh (7)
Insert mesh lines between all cells:
Insert 15 row mesh lines and 5 column mesh lines:
Insert mesh lines around the first 10 columns:
Use a sequence of colors for the mesh lines:
Insert mesh lines after the first and second rows:
Use MeshAutomatic to draw mesh for the data in a ragged array:
Use Mesh"Nonzero" to draw mesh lines around nonzero cells:
PlotLegends (5)
Generate a legend automatically:
PlotLegends automatically picks up ColorFunction:
Legend uses ColorRules as labels:
Use Placed to place legend outside the plot:
PlotRange (5)
Plot only elements with values up to 3, leaving the rest white:
The first two entries in PlotRange specify the range of rows and columns to include:
With specific plot range {amin,amax}, the colors range from white at amin to black at amax:
Applications (11)
Plot a two-color cellular automaton evolution:
Plot a three-color cellular automaton evolution:
Use colors rather than gray levels:
Plot the imaginary parts of a Vandermonde matrix for a discrete Fourier transform:
Plot the inverse of a matrix, shading according to absolute value:
Show positive entries as black and others as yellow:
Plot a table of values of five sine waves in random directions:
Use a special color for non-numeric data:
Properties & Relations (8)
An empty array yields a blank picture:
Grid arranges elements the same way as ArrayPlot:
Raster arranges elements upside down and with colors reversed relative to ArrayPlot:
Make the array be shown the same way as in ArrayPlot:
Use ArrayPlot3D for 3D arrays of data:
Use MatrixPlot when entries have a big range and many different values:
Use ReliefPlot for medical and geographic data:
Use ListDensityPlot for structured or unstructured data sampled from continuous densities:
Use GraphPlot for visualizing adjacency matrices:
Possible Issues (2)
ArrayPlot may not be able to distinguish between large numbers of different values:
Use MatrixPlot instead (or provide a custom ColorFunction):
Entries of very small relative absolute values may not be differentiable from zero:
MatrixPlot scales entries so that entries with small relative absolute values can still be seen:
History
Introduced in 2004 (5.1) | Updated in 2007 (6.0) ▪ 2012 (9.0) ▪ 2014 (10.0) ▪ 2020 (12.1) ▪ 2021 (12.3) ▪ 2025 (14.3)
Text
Wolfram Research (2004), ArrayPlot, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ArrayPlot.html (updated 2025).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2004. "ArrayPlot." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2025. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ArrayPlot.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2004). ArrayPlot. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ArrayPlot.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_arrayplot, author="Wolfram Research", title="{ArrayPlot}", year="2025", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ArrayPlot.html}", note=[Accessed: 03-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_arrayplot, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={ArrayPlot}, year={2025}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ArrayPlot.html}, note=[Accessed: 03-March-2026]}