BubbleChart[{{x1,y1,z1},{x2,y2,z2},…}]
makes a bubble chart with bubbles at positions {xi,yi} with sizes zi.
BubbleChart[{…,wi[{xi,yi,zi},…],…,wj[{xj,yj,zj},…],…}]
makes a bubble chart with bubble features defined by the symbolic wrappers wk.
BubbleChart[{data1,data2,…}]
makes a bubble chart from multiple datasets datai.




BubbleChart
BubbleChart[{{x1,y1,z1},{x2,y2,z2},…}]
makes a bubble chart with bubbles at positions {xi,yi} with sizes zi.
BubbleChart[{…,wi[{xi,yi,zi},…],…,wj[{xj,yj,zj},…],…}]
makes a bubble chart with bubble features defined by the symbolic wrappers wk.
BubbleChart[{data1,data2,…}]
makes a bubble chart from multiple datasets datai.
Details and Options




- Data elements for BubbleChart can be given in the following forms:
-
{xi,yi,zi} a pure bubble value {Quantity[xi,ux],Quantity[yi,uy],Quantity[zi,uz]} a bubble value with units <|kxxi,kyyi,kzzi|> association of keys and bubble value wi[{xi,yi,zi},…] a bubble with value {xi,yi,zi} and wrapper wi formi->mi a bubble form with metadata mi - The values zi should be positive.
- Data not given in these forms is ignored in forming the bubble chart.
- Datasets for BubbleChart can be given in the following forms:
-
{e1,e2,…} list of elements with or without wrappers <|k1e1,k2e2,…|> association of keys and values TimeSeries[…],EventSeries[…],TemporalData[…] time series, event series, and temporal data WeightedData[…] augmented datasets w[{e1,e2,…},…] wrapper applied to a whole dataset w[{data1,data1,…},…] wrapper applied to all datasets - BubbleChart[Tabular[…]cspec] extracts and plots values from the tabular object using the column specification cspec.
- The following forms of column specifications cspec are allowed for plotting tabular data:
-
{colx,coly,colz} plot data from columns x. y and z {{colx1,coly1,colz1},{colx2,coly2,colz2},…} plot multiple sets of columns - The following wrappers can be used for chart elements:
-
Annotation[e,label] provide an annotation Button[e,action] define an action to execute when the element is clicked Callout[e,label] display the element with callout labeling EventHandler[e,…] define a general event handler for the element Hyperlink[e,uri] make the element act as a hyperlink Labeled[e,…] display the element with labeling Legended[e,…] include features of the element in a chart legend Mouseover[e,over] make the element show a mouseover form PopupWindow[e,cont] attach a popup window to the element StatusArea[e,label] display in the status area when the element is moused over Style[e,opts] show the element using the specified styles Tooltip[e,label] attach an arbitrary tooltip to the element - In BubbleChart, Labeled, Callout and Placed allow the following positions:
-
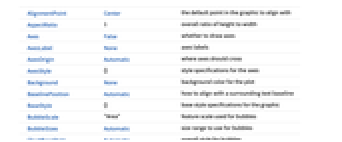
Top,Bottom,Left,Right,Center positions within bubbles Above,Below, Before, After positions outside bubbles {{bx,by},{lx,ly}} scaled position {lx,ly} in the label at scaled position {bx,by} in the bubble - BubbleChart has the same options as Graphics with the following additions and changes: [List of all options]
-
AspectRatio 1 overall ratio of height to width BubbleScale "Area" feature scale used for bubbles BubbleSizes Automatic size range to use for bubbles ChartBaseStyle Automatic overall style for bubbles ChartElementFunction Automatic how to generate raw graphics for bubbles ChartElements Automatic graphics to use for each of the bubbles ChartLabels None labels for data elements and datasets ChartLegends None legends for data elements and datasets ChartStyle Automatic style for bubbles ColorFunction Automatic how to color bubbles ColorFunctionScaling True whether to normalize arguments to ColorFunction Frame True whether to draw a frame around the chart LabelingFunction Automatic how to label bubbles LabelingSize Automatic maximum size of callouts and labels LabelingTarget Automatic how to determine automatic label positions LegendAppearance Automatic overall appearance of legends PerformanceGoal $PerformanceGoal aspects of performance to try to optimize PlotInteractivity $PlotInteractivity whether to allow interactive elements PlotTheme $PlotTheme overall theme for the chart ScalingFunctions None how to scale individual coordinates TargetUnits Automatic units to display in the chart - BubbleChart layers bubbles from largest to smallest for maximal visibility.
- The arguments supplied to ChartElementFunction are the bubble region {{xmin,xmax},{ymin,ymax}}, the values {xi,yi,zi}, and the metadata {m1,m2,…} from each level in a nested list of datasets.
- A list of built-in settings for ChartElementFunction can be obtained from ChartElementData["BubbleChart"].
- The arguments supplied to ColorFunction are x, y, and z.
- Chart feature themes affect the data's graphic styling. Themes include:
-

"BoldScheme" bold elements from Chart Element Schemes 
"FadeScheme" faded elements from Chart Element Schemes - Style and other specifications from options and other constructs in BubbleChart are effectively applied in the order ChartStyle, ColorFunction, Style and other wrappers, ChartElements, and ChartElementFunction, with later specifications overriding earlier ones.
-
 Highlight options with settings specific to BubbleChart
Highlight options with settings specific to BubbleChart
-
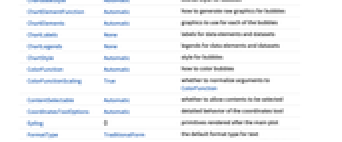
AlignmentPoint Center the default point in the graphic to align with AspectRatio 1 overall ratio of height to width Axes False whether to draw axes AxesLabel None axes labels AxesOrigin Automatic where axes should cross AxesStyle {} style specifications for the axes Background None background color for the plot BaselinePosition Automatic how to align with a surrounding text baseline BaseStyle {} base style specifications for the graphic BubbleScale "Area" feature scale used for bubbles BubbleSizes Automatic size range to use for bubbles ChartBaseStyle Automatic overall style for bubbles ChartElementFunction Automatic how to generate raw graphics for bubbles ChartElements Automatic graphics to use for each of the bubbles ChartLabels None labels for data elements and datasets ChartLegends None legends for data elements and datasets ChartStyle Automatic style for bubbles ColorFunction Automatic how to color bubbles ColorFunctionScaling True whether to normalize arguments to ColorFunction ContentSelectable Automatic whether to allow contents to be selected CoordinatesToolOptions Automatic detailed behavior of the coordinates tool Epilog {} primitives rendered after the main plot FormatType TraditionalForm the default format type for text Frame True whether to draw a frame around the chart FrameLabel None frame labels FrameStyle {} style specifications for the frame FrameTicks Automatic frame ticks FrameTicksStyle {} style specifications for frame ticks GridLines None grid lines to draw GridLinesStyle {} style specifications for grid lines ImageMargins 0. the margins to leave around the graphic ImagePadding All what extra padding to allow for labels etc. ImageSize Automatic the absolute size at which to render the graphic LabelingFunction Automatic how to label bubbles LabelingSize Automatic maximum size of callouts and labels LabelingTarget Automatic how to determine automatic label positions LabelStyle {} style specifications for labels LegendAppearance Automatic overall appearance of legends Method Automatic details of graphics methods to use PerformanceGoal $PerformanceGoal aspects of performance to try to optimize PlotInteractivity $PlotInteractivity whether to allow interactive elements PlotLabel None an overall label for the plot PlotRange All range of values to include PlotRangeClipping False whether to clip at the plot range PlotRangePadding Automatic how much to pad the range of values PlotRegion Automatic the final display region to be filled PlotTheme $PlotTheme overall theme for the chart PreserveImageOptions Automatic whether to preserve image options when displaying new versions of the same graphic Prolog {} primitives rendered before the main plot RotateLabel True whether to rotate y labels on the frame ScalingFunctions None how to scale individual coordinates TargetUnits Automatic units to display in the chart Ticks Automatic axes ticks TicksStyle {} style specifications for axes ticks
List of all options
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (3)
Scope (32)
Data and Wrappers (14)
Items in a dataset are colored the same:
Nonreal data is taken to be missing:
The time stamps in TimeSeries, EventSeries, and TemporalData are ignored:
The values in associations are taken as bubble values:
Associations can be nested down to the point level:
The weights in WeightedData are ignored:
Use wrappers on individual data, datasets, or collections of datasets:
Override the default tooltips:
Use any object in the tooltip:
Use PopupWindow to provide additional drilldown information:
Button can be used to trigger any action:
Tabular Data (1)
Styling and Appearance (8)
Use an explicit list of styles for the bubbles:
Use any gradient or indexed color schemes from ColorData:
Use color schemes designed for charting:
ChartBaseStyle can be used to set an initial style for all chart elements:
Style can be used to override styles:
Use any graphic for pictorial bubbles:
Use built-in programmatically generated bubbles:
For detailed settings, use Palettes ▶ ChartElementSchemes:
Use a theme with simple ticks and grid lines in a bright color scheme:
Use a theme with a high contrast color scheme and 3D bubbles:
Labeling and Legending (9)
Use Labeled to add a label to a bubble:
Use symbolic positions for label placement:
Use Placed to control the positioning of labels, using the same positions as for Labeled:
Provide value labels for bubbles by using LabelingFunction:
Specify the maximum size of labels:
For dense sets of points, some labels may be turned into tooltips by default:
Increasing the size of the plot will show more labels:
Use legend entries for different datasets:
Use Legended to add additional legend entries:
Use Placed to affect the positioning of legends:
Options (129)
AspectRatio (3)
By default, BubbleChart uses the same width and height:
Use a numerical value to specify the height to width ratio:
AspectRatioAutomatic determines the range from the values:
Axes (3)
By default, BubbleChart uses a frame instead of axes:
AxesLabel (4)
AxesOrigin (2)
AxesStyle (4)
BubbleScale (2)
ChartBaseStyle (5)
Use ChartBaseStyle to style all bubbles:
ChartBaseStyle combines with ChartStyle:
ChartStyle may override settings for ChartBaseStyle:
ChartBaseStyle combines with Style:
Style may override settings for ChartBaseStyle:
ChartBaseStyle combines with ColorFunction:
ColorFunction may override settings for ChartBaseStyle:
ChartElementFunction (5)
Get a list of built-in settings for ChartElementFunction:
For more settings, use Palettes ▶ ChartElementSchemes:
Write a custom ChartElementFunction:
Use metadata passed on from the input, in this case charting the data:
The built-in element function may have options; use Palettes ▶ ChartElementSchemes to set them:
ChartElements (5)
Create a pictorial chart based on any Graphics object:
Use a different graphic for each dataset:
Styles are inherited from styles set through ChartStyle etc.:
Explicit styles set in the graphic will override other style settings:
ChartLabels (7)
By default, labels are placed in the bubbles:
Labeled wrappers in data will place additional labels:
Use Placed to control label placement:
Coordinate-based placement relative to a bubble:
Place all labels at the center of each bubble and vary the coordinates within the label:
Use the third argument to Placed to control formatting:
Use Callout to connect the labels to the bubbles:
ChartLegends (7)
ChartStyle (14)
Use ChartStyle to set the style:
Use "Gradient" colors from ColorData:
Use "Indexed" colors from ColorData:
Style both rows and columns of data:
With both row and column styles, the last style may override earlier ones:
Style overrides settings for ChartStyle:
Style may combine with ChartStyle:
ColorFunction overrides settings for ChartStyle:
ColorFunction may combine with ChartStyle:
ChartElements may override settings for ChartStyle:
ColorFunction (3)
Use ColorFunctionScaling->False to get unscaled height values:
ColorFunction overrides styles in ChartStyle:
Use ColorFunction to combine different style effects:
ColorFunctionScaling (2)
Frame (4)
BubbleChart uses a frame by default:
Use FrameFalse to turn off the frame:
FrameLabel (4)
FrameTicks (7)
Frame ticks are placed automatically by default:
By default, the top and right edges have tick marks but no tick labels:
Use All to include tick labels on all edges:
Place tick marks at the specified positions:
Draw frame tick marks at the specified positions with specific labels:
Specify tick length as a fraction of the size of the chart:
Use different sizes in the positive and negative directions for tick marks:
FrameTicksStyle (3)
ImageSize (7)
Use named sizes such as Tiny, Small, Medium and Large:
Specify the width of the plot:
Specify the height of the plot:
Allow the width and height to be up to a certain size:
Specify the width and height for a graphic, padding with space if necessary:
Setting AspectRatioFull will fill the available space:
Use maximum sizes for the width and height:
Use ImageSizeFull to fill the available space in an object:
Specify the image size as a fraction of the available space:
LabelingFunction (7)
Use automatic labeling by values through Tooltip and StatusArea:
Use Placed to control label placement:
Coordinate-based placement relative to a given bubble:
Use Callout to place labels automatically:
Use symbolic positions to place Callout labels:
Control the formatting of labels:
Use the given chart labels as arguments to the labeling function:
LabelingSize (4)
LabelingTarget (7)
Labels are automatically placed to maximize readability:
Use a denser layout for the labels:
Show the quarter of the labels that are easiest to read:
Only allow labels that are orthogonal to the points:
Only allow labels that are diagonal to the points:
Restrict labels to be above or to the right of the points:
PerformanceGoal (1)
PlotInteractivity (4)
Ticks (6)
Ticks are placed automatically in each chart:
Use TicksNone to draw axes without any tick marks:
Place tick marks at the specified positions:
Draw tick marks at the specified positions with specific labels:
Specify the lengths for ticks as a fraction of graphics size:
Use different sizes in the positive and negative directions for ticks:
Applications (5)
Display GDP per capita, poverty fraction and population for countries in Africa:
Define a labeling function for more complex tooltips:
Mouse over the bubbles to view a country's data:
Display oil data for the G15 countries using PieChart for bubbles to indicate import and export:
Click the bubbles to hear the name of the country, its GDP per capita and its population:
Get population, weather and coordinate data of large Japanese cities:
Mouse over the bubbles to get city and temperature information:
Represent clusters of elements based on three properties:
Cluster the elements into groups based on the value of their properties:
Properties & Relations (2)
Use BubbleChart3D to get a 3D rendering of bubble charts:
Use SectorChart3D and RectangleChart3D as alternative visualizations:
See Also
ListPlot ListPlot3D ListDensityPlot BubbleChart3D SectorChart BarChart GeoBubbleChart
Function Repository: ComplexBubblePlot
History
Introduced in 2008 (7.0) | Updated in 2010 (8.0) ▪ 2012 (9.0) ▪ 2014 (10.0) ▪ 2017 (11.1) ▪ 2018 (11.3) ▪ 2025 (14.2) ▪ 2025 (14.3)
Text
Wolfram Research (2008), BubbleChart, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BubbleChart.html (updated 2025).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2008. "BubbleChart." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2025. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BubbleChart.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2008). BubbleChart. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BubbleChart.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_bubblechart, author="Wolfram Research", title="{BubbleChart}", year="2025", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BubbleChart.html}", note=[Accessed: 24-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_bubblechart, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={BubbleChart}, year={2025}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BubbleChart.html}, note=[Accessed: 24-February-2026]}